Many machines are designed with the help of ball bearings, which provide easy rotational movement to those. Ball bearings are preferred in quite a few industries, such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics, due to their strength, reliability, and versatility. As per the required use, the designs and application of the ball bearings differ. Ball bearings are incredibly diverse; their features vary greatly, and they serve a variety of roles within the context of each system, including performance and efficiency. In other words, any new device or machinery manufactured contains these ball bearings, and knowing them makes it easier for a reader to know how the machine and device work.
What is a Ball Bearing, and How Does it Work?
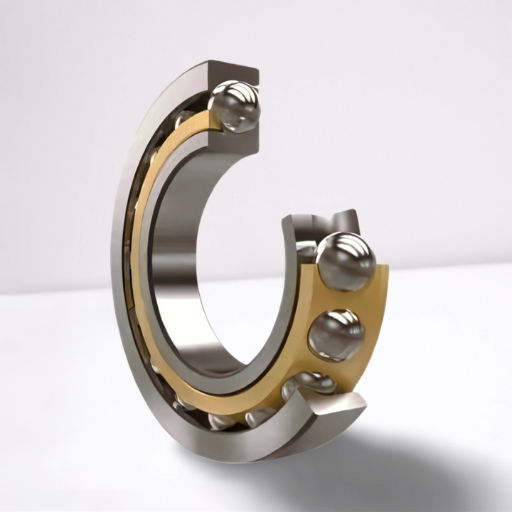

Ball bearings are essential parts of various machines and other modern devices designed for smooth rotation. It comprises a pair of rings with a number of balls contained between them, with some applications requiring a cage to provide spacing. These tiny balls remove friction, which enables an apparatus to function both efficiently and durably while also extending its performance. Because of this, ball bearings are commonly found in many day-to-day devices as well as industrial machines.
Types of Ball Bearings
There are multiple varieties of ball bearings, and each type is designed to fulfill a certain purpose. I, as a specialist in the field, usually focus on distinguishing four main bearing types:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings – These are the most common type of all, as they can accommodate both radial and axial loads. These are widely utilized in home appliances and automobile engines due to their sustainability and simple structure.
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings – This type of bearing can support combined loads and requires higher precision and higher speed, which makes it a suitable option for any aerospace or robotic-engineered component.
- Self-Aligning Ball Bearings -These are perfectly designed for the case in which a shaft is subject to angular misalignment of a few degrees, they incorporate two rows of balls and a single spherical raceway which enables an efficient operation under harsh environments.
- Thrust Ball Bearings – These bearings are designed on the sole basis of anti-axial loads. These bearings are more suited for low-speed operations like automotive pressing systems or rotary tables.
Every type is unique, and its application is intended for specific operational requirements, so the selection of the correct ball bearing is consistent with the operational demands you are dealing with.
How Ball Bearings Reduce Friction
By reducing the contact area between two moving parts, ball bearings lower friction. Unlike two surfaces sliding against each other, which generates a high friction contact, the bearing employs spherical balls to roll between the inner and outer surfaces of the cylinder. Sliding contact is greatly reduced by rolling contact which is what opens a wider range of movement to iron bearings.
The following factors help in easing friction, and they include:
- Surface Contact – The use of ball bearings replaces sliding contact with rolling contact which greatly diminishes the contact area to prevent excessive friction. This design also guarantees that little energy is required to overcome resistance.
- Material Quality – Stainless steel and ceramic are the most used materials in the manufacture of ball bearings. These materials are sturdy, smooth, and have high wear resistance, thus minimizing friction with the passing of time.
- Lubrication –Lubrication goes a long way in minimizing friction. A thin film of oil or grease dished out between the balls and the raceways ensures complete wear of the surface and motion of the bearing. This increases the life span of the bearing.
- Precision Engineering –Ball bearings greatly reduce uneven forces, as the balls are manufactured with great precision and engage snugly in the raceways, thereby ensuring smooth rolling friction.
- Load Distribution – The balls being spherical in shape provides good load distribution, thus relieving the individual parts from excessive stressing and easing the working.
With all of those factors combined, ball bearings are able to perform very well, all while reducing energy losses due to friction. And this is precisely why they are widely used in numerous mechanical applications!
Common Applications of Ball Bearings
ball bearings are useful in a number of ways and are crucial to many tools in different industries. For instance, in vehicles, bearings are critical for facilitating the smooth spinning of the wheels as well as the effective functioning of gearboxes. In the same fashion, industrial machinery is able to perform speedy operations with very minimal wear due to the use of ball bearings, which in turn leads to greater productivity. Even in smaller devices such as fans, computer hard disks, and household appliances, ball bearings are vital in improving quieter operations and durability. From aerospace and medical apparatus, these components are the unspoken heroes that help the devices operate.
Exploring Different Types of Ball Bearings
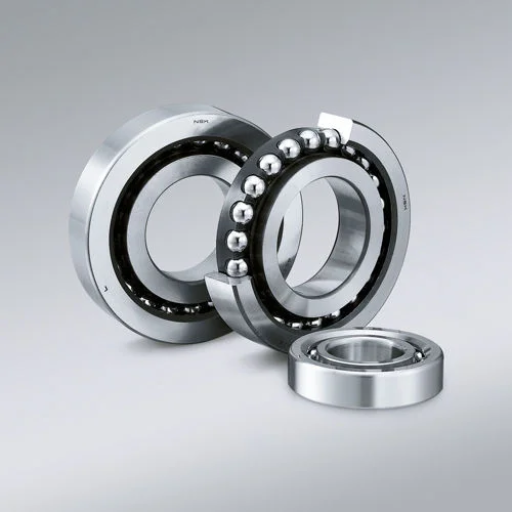

To reduce friction between rotating parts in machinery, multiple types of ball bearings are used. The construction and recoil of advanced rotary machines demand specialized devices, and ball bearings, in turn, are tailor-made for different usages. For example, self-aligning ball bearings can be employed for conveyor belt systems, while thrust ball bearings can be used for aircraft and automobiles. Angular contact ball bearings can also be employed, as they can bear both radial and axial thrust. Deep Groove Ball bearings are the most versatile and widely used since they can fit in electric motors as well as domestic appliances.
Characteristics of Deep Groove Ball Bearings
out of all bearings, deep groove ball bearings are among the most common and most reliable. They carry both axial and radial loads due to their deep raceways and allow high-speed operations. The bearing’s simple structure guarantees durability as well as low maintenance while providing low friction. From my experience, they excel in applications ranging from electric motors to household appliances, offering consistent performance and long service life. In addition to these factors, the deep groove ball bearings accommodate misalignment to a certain degree, which in turn makes usage in real life much easier.
Advantages of Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Angular Contact Ball Bearings are preferred as they are excellent in providing both radial and axial loads, sometimes at the same time. The configuration ensures optimal load distribution which provides both high speed and high performance stability and accuracy. Furthermore, their strength, energy efficiency, and self-alignment capability allow for more extensive application in the automotive, manufacturing, and home appliance industries.
Understanding Thrust Bearings and Their Uses
See, with thrust bearings; there are so many experiences of how helpful they can be in controlling axial loads especially. Other types of bearings are designed to carry radial and axial loads equally, so it suffices to say that thrust bearings are solely designed to bear axial loads only.
In simpler terms, this is how we analyze thrust bearings and their implementation:
- Load Capacity – One of the vital factors affecting the load-bearing capacity of a thrust bearing is the type of bearing. For example, ball thrust bearings are more suited for low to medium loads, while roller thrust bearings are intended for high loads and applications.
- Speed Performance – For high-speed applications, material properties and lubrication become critical. Good design practices ensure that efficient operation can take place with minimal amount of heat being produced.
- Alignment Tolerance – Many of the thrust bearings self-align or have spherically seated features. This important feature allows the bearing to compensate for misalignment of the shaft which is helpful in minimizing wear during operation.
- Material Durability – This type of bearings is frequently built with durable materials, such as hardened steel, which allows them to endure continuous stress without becoming deformed or damaged.
- Applications – Thrust bearings are widely used, for example, in automotive systems for transmission of rotation affected by axial loads. In the same way, they are also important in turbines, pumps, and marine equipment, allowing the equipment to work without interruptions.
I will forever stress the importance of picking the right bearing type and size according to parameters such as load, speed, and alignment because it can significantly boost performance and efficiency levels. It is very interesting how such a simple part can work so easily in very intricate machines!
How to Choose the Right Bearing for Your Needs

To select the appropriate bearing, first evaluate the load characteristics of the application: radial, axial, and/or a combining load. Next, check the intended speed and make sure that the bearing selected will be able to work efficiently at that speed. Furthermore, factors such as temperature, humidity, and contaminants should also be considered since these would affect the choice of sealing and materials. Also, alignment and space limitations will help in specific bearing type selection, where ball bearings may be used in precision applications, while roller bearings may be more effective in applications requiring larger loads. Lastly, make sure that the selected bearings are suitable for the lubrication structure in order to ensure longer service life and functionality.
Factors to Consider: Radial and Axial Load
In my bearing selection process, radial and axial loads begin by evaluating the application conditions. Radial load mainly acts at right angles to the shaft, while axial load acts parallel to the axis. It will also be vital to determine these forces reliably for proper comparison with the bearing load ratings. For a bearing subjected to more radial loads, deep groove ball bearings or cylindrical roller bearings are usually the best ones. On the other hand, large axial loads can be supported by angular contact ball bearings or thrust bearings. If, in some instances, both types of loads are to be considered, then special bearings like tapered roller bearings may be required to give the best results.
Importance of Low Friction in Bearing Selection
I have no doubt in saying that a focus on low friction as a priority when selecting bearings is beneficial for both efficiency and longevity. Key to high-speed or precise applications, low-friction bearings substantially lessen energy losses. Heat loss and the heat produced in the particular bearing can be reduced by reducing the friction which then improves the initiating performance and lengthens the life span of the bearing while reducing maintenance. My experience has been that picking appropriate low-friction materials and designs lowers life cycle costs while making the operation smoother and reducing system impacts.
Assessing High-Speed Applications for Ball Bearings
When evaluating ball bearings used in high-speed applications, I always take a number of crucial parameters to ensure optimum performance and reliability. This time I would highlight a few factors which I would suggest considering.
- Speed Rating: As for the components of the bearing, its speed rating is the most crucial. It is established by the number of revolutions of the shaft that the bearing can sustain without any damage. I examine the manufacturer’s specifications accordingly with the type of cage and lubrication types.
- Material Selection: In the case of high-speed applications, the material of the ball and raceway is very critical. Quality steel or ceramic materials are preferred, especially because they can take a large magnitude of force, have lower friction, and are less prone to wear and tear.
- Lubrication: At high velocities, the bearings should be properly lubricated to ensure that their efficiency is retained, for low speeds of operation, some amount of friction is tolerable, but as the speed increases friction must be eliminated, this is… I have used high-performance lubricants that are suitable for heavy loads and high temperatures, as a lack of sufficient lubricants can cause overheating and an early breakdown.
- Bearing Design: The self arrangement of each individual bearing is important also. When I have to deal with high-speed operations, I consider the use of engineered bearings, which have strong cage designs to dampen oscillations during rotation for added stability.
- Load Carrying Capacity: While working at higher speeds, the bearings, in this case, are required to bear the loads that are applied to them. The inability to properly manage the loads could result in excessive wear of the bearing, which in turn reduces its lifespan.
- Heat Dissipation: The high-speed movement causes a rise in temperature, which may affect the bearing failure. I assess the thermal aspects of the system and take into account such features as heat-resistant components or cooling devices to avoid overheating.
With the aid of stringent analysis of these parameters, I am in a position to recommend ball bearings required for applications where high speed is irrevocable without compromising on durability and efficiency as well as performance.
The Role of Deep Groove Ball Bearings in Machinery
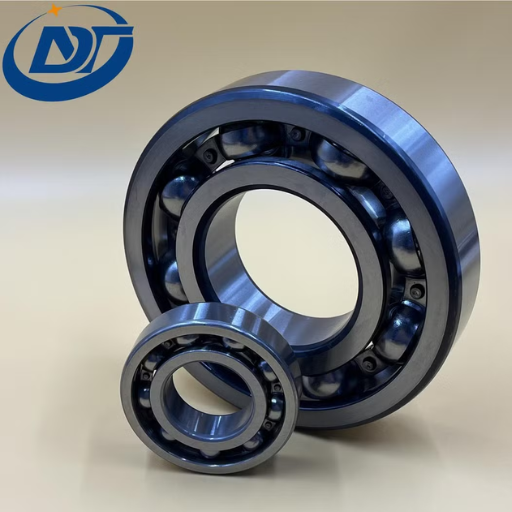
Deep Groove Ball Bearings are highly useful to machines and provide low friction and smooth rotation. One of their interesting features is that they are capable of transmitting any combination of radial and axial force while still being functional. Being quite robust and efficient, these bearings are used in a variety of apparatuses ranging from small electric motors to big industrial ones, where their size, precision, and effectiveness are of great importance.
Design and Function of Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Deep Groove Ball Bearings are designed fairly simply and consist of four key components such as an inner ring, an outer ring, a cage, and rolling elements. The deep raceway grooves are in close proximity to the radius of the balls; hence, they are able to facilitate the transferring of radial and axial loads onto the bearing effectively. Such an arrangement helps to reduce friction, reduce heat, and allows for high speed of operation, this makes them reliable for many applications requiring precision and long service life.
Why Deep Groove Bearings are Popular in Industries
From my industry experience, the reason why deep groove ball bearings are widely utilized in many industries is due to their adaptability, durability and outstanding efficiency. Here’s a more specific explanation of why these bearings are so widely adopted:
- Versatile Load Handling
Deep groove ball bearings can handle radial and axial loads in an effective manner. Such means gives them an extensive operational range suited for all kinds of applications from relatively low-load household appliances to high-load equipment in industrial settings.
- High-Speed Performance
Low friction has always been their trademark, allowing them to perform operations smoothly and efficiently, even at high speeds. The reduced friction translates into less wear and tear, therefore resulting in a bearable lifespan and dependability in operations that require consistent speed, such as automobiles and motors.
- Durability and Longevity
These bearings are tough and would last long since they are made from materials that can withstand wear, corrosion, and heat. The precision design achieves the desired results of excessive wear and tear while surviving thorny surroundings.
- Low Maintenance Requirements
Users and manufacturers alike save time and money due to a straightforward design that does not have free-moving parts or components requiring high maintenance of deep groove ball bearings. Their grease-sealed variants are additionally safeguarded against contaminants, thus further improving their performance.
- Compact Design
For bearings that are relatively more load-bearing and stronger, these are rather small in size. This means squeezing the bearings into tight spaces is possible, which is a necessity where space is a restriction but performance isn’t.
- Cost-Effectiveness
Given their extended service life, high reliability, and low maintenance cost, deep groove bearings are considered very economical for industrial applications. So, investors definitely regard them as a good option and investment.
These characteristics of deep groove ball bearings explain why they can be found in all sectors ranging from manufacturing to automotive and many others. Their sustained usage as a bearing type greatly speaks for their excellent design and versatility.
Understanding Stainless Steel Bearings and Their Benefits

I can certainly say without fear of contradiction that stainless steel bearings are the future in many industries. Firstly, they are corrosion resistant, which makes them suitable in instances where there is the presence of moisture, chemicals, or extreme heat. Furthermore, from my experience, their performance in such harsh environments allows the equipment to last longer, hence reducing the downtime and repair costs. Moreover, stainless steel bearings provide great strength and efficiency, making them suitable for straining industrial faces as well as precision-filled applications. These bearings are certainly wise bearings for any firm that is looking forward to the longevity of its operations.
Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steel Bearings
It is evident that the corrosion resistance of stainless steel bearings can be attributed to the specific characteristics of the material itself. Let us analyze in detail the major parameters that assist them in their functioning in this respect:
- Chromium Content
Its needle roller bearings are composed of stainless steel, which is most commonly a chromium-containing alloy since they are covered with a thin passive protective oxide layer. The passive layer greatly protects from oxidation and rusting, even in highly oxidizing environments.
- Resistance to Moisture
Stainless steel bearings are highly moisture resistant, unlike other materials that are vulnerable to moisture and water. Stainless steel bearings are ideal for use in marine environments, the food processing industry, and any other environment that is at risk of coming into contact with water.
- Chemical Resistance
It also has regard more than such product protection from chemicals thus improving its usefulness in clothes that are exposed to harsh chemicals such as acids, alkaline materials, and cleansing agents as well. All such chemicals are used in pharmaceutical and petrochemical industries and even while treating wastewater.
- Temperature Stability
For instance, stainless steel bearings can also be utilized without any fear, even in areas with highly fluctuating temperatures. Its special quality makes it possible to function perfectly even in applications employing very high or low temperatures, further enhancing its usability in various industries.
- Low Maintenance Requirements
Robust and wearing-out resistant materials are usually used in making them, thus minimizing rusting and wearing off. This means that the bearings will not require frequent maintenance and replacement, thus reducing operational costs in the long term. This is especially important in cases where uptime needs to be maintained at all costs.
Stainless steel bearings may be considered as having a long and dependable stance since they do not wear and tear too much, even under extreme conditions, if all the specifications are met. If corrosion resistance is the most important aspect of any branch, then these bearings are the best in the trade.
Durability and Longevity of Bearings Made from Stainless Steel
Stainless steel bearings might be on the pricier side, but trust them to be cost-effective in the long run. This is because they are exceptionally durable and are quite resistant to rust, harsh mechanical usage, and high temperatures. The best thing about steel bearings is that they reduce your operational maintenance which makes them ideal for trustful industries. In short, steel bearings ensure long viability and are easy to maintain, this means that they are a perfect cost-effective solution in the long term.
Reference
- General Theory and Application to Ball Bearings | J. Tribol – This source provides a mathematical model for calculating equilibrium and load distribution in ball bearings.
- Fatigue life and fatigue reliability mechanism of ball bearings – This paper analyzes the effects of external loads on the mechanical properties and fatigue life of ball bearings.
- History of Ball Bearings – This document covers the historical industrial applications of ball bearings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are ball bearings, and how are they used in various applications?
A: Ball bearings are a type of rolling-element bearing that use balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races. They are widely used in various applications due to their ability to support both radial and axial loads, reduce friction, and enhance the efficiency of machinery.
Q: What is an angular contact bearing,g, and where is it commonly used?
A: An angular contact bearing is a type of ball bearing designed to handle both radial and axial loads. It is commonly used in applications that require high-speed performance and precision, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Q: How do miniature bearings differ from standard bearings?
A: Miniature bearings are smaller in size compared to standard bearings and are used in applications where space is limited. Despite their size, they maintain high precision and are often used in medical devices, robotics, and electronic equipment.
Q: What is the purpose of a flanged bearing?
A: A flanged bearing features an extended lip or flange that provides additional support and easy mounting. These bearings are ideal for applications where precise alignment is critical, such as in conveyor systems and automotive applications.
Q: Can you explain the function of single-row angular contact ball bearings?
A: Single-row angular contact ball bearings are designed to accommodate axial loads in one direction and provide high precision and speed capabilities. They are commonly used in pumps, compressors, and high-speed machinery.
Q: Why are radial ball bearings widely used in machinery?
A: Radial ball bearings are used due to their ability to support radial loads and reduce friction in rotating parts. They are versatile and find applications in everything from electric motors to household appliances.
Q: What are the advantages of using hybrid ball bearings?
A: Hybrid ball bearings include ceramic balls which reduce the coefficient of friction, increase speed, and enhance longevity. They are used in high-performance applications such as electric motors and turbines, where efficiency and durability are crucial.
Q: How do rolling-element bearings support various loads?
A: Rolling-element bearings consist of rolling elements, such as balls or rollers, that allow for smooth motion between two surfaces. They support loads by distributing weight evenly and minimizing friction, which enhances performance and reliability in machinery.
Q: What factors should be considered when selecting a ball bearing?
A: When selecting a ball bearing, factors such as load capacity, speed, precision, size, and the width of the bearing should be considered. The specific requirements of the application and environmental conditions also play a crucial role.
