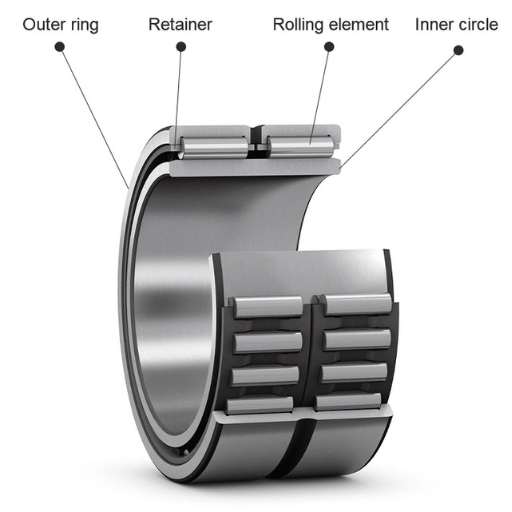
Roller bearings come together to create a distinctive assembly referred to as needle roller bearings whose components help in fitting various machines. In simple terms, if the need to lift heavy objects in a confined space arises, they can be comfortably lifted with the aid of needle roller bearings. These bearings are some of the most frequently used items in a multitude of industries ranging from aerospace to automotive, manufacturing, and printing. These bearings come with special steel axles that are designed to take in high torque and cater to vertical assembly. This article outlines the key features as well as the applications of needle roller bearings and their ascension in the world of machinery.
What is a Needle Roller Bearing?
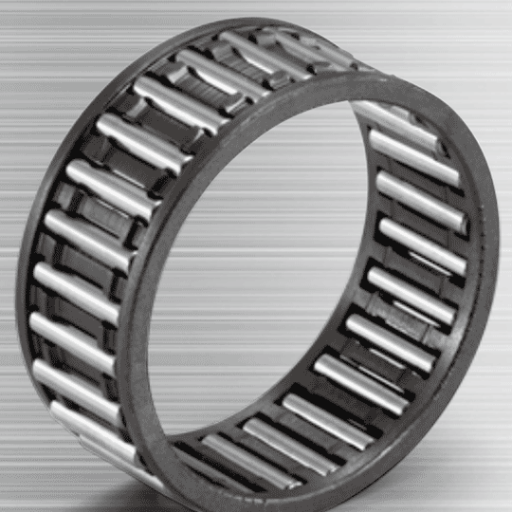

A needle roller bearing is classified as a type of roller bearing that has long, thin, cylindrical rollers that rotate. Their main purpose is to decrease friction while supporting significantly high-bearing loads in compact designs. Since these bearings can withstand high radial loads in relation to their size, these bearings are frequently employed when the amount of space available is small, but the performance and reliability of the bearing are vital.
Characteristics of Needle Roller Bearings
As someone who has worked in this industry for a while, I can comfortably say that needle roller bearings are relatively small but incredibly strong in their construction. This type of bearing has long, slender rollers that can be around 3-10 times its diameter, which makes it easy for effective load distribution with minimum friction. One of their key characteristics is the ability to carry high radial loads; such applications are commonly limited in space but need to be reliably engineered. Besides, their great durability coupled with wear-resisting properties guarantees a long lifespan even under tough working conditions. Such units can be catered to different categories, such as caged, full complement, or drawn cup, and can be used in a wide range of industries. Needle roller bearings can potentially offer great value in terms of efficiency while working in precision.
How Needle Roller Bearings Differ from Other Bearings
The primary difference between needle roller bearings and other types of bearings is that they use elongated cylindrical rollers instead of ball bearings. This feature offers greater load-bearing capacity. With this configuration, they are able to endure a heavier load than a ball bearing of equal size whilst still having a small size. A needle roller certainly excels when space is at a premium, but durability and load capacity are essential, unlike standard rollers or ball bearings. Their unique shapes help them reduce friction best in high-speed, high-load conditions.
Common Applications of Needle Bearings
Based on what I have witnessed, the use of needle bearings is fundamental in automotive transmissions in situations that require space and efficiency. Medium speeds and heavy loads could be surmounted with ease thanks to these types of bearings which have a very compact design. Similarly, they are fundamental in robotics and power tools as they provide accuracy and reliability in tough situations. I have also witnessed the application of needle bearings in aerospace components as well as in industrial machinery, where performance under extreme stresses was a prerequisite. Because of their adaptability, they provide a critical solution in any industry that requires performance together with compactness.
How Do Needle Bearings Reduce Friction?

Needle bearings lessen friction by using many little cylindrical rollers to lift weight and lessen the contact surface between moving parts. In my opinion, their design is such that with less room, they can accommodate more load-carrying capacity than conventional bearings, which makes them very effective in restricted areas. Proper alignment of the needles limits wear and tear of the surfaces and enables smooth movement even in stressful conditions. Reliability and strength are the reasons why I normally propose the use of needle bearings in situations where prolonged service and high operation efficacy requirements are needed.
The Role of the Cage in Friction Reduction
The cage in a needle bearing has some important roles in reducing friction, and I would like to explain this slowly and in detail. First, the purpose of the cage is to separate the individual needles from each other. Otherwise, if it is not provided, it would allow the needles to rub against each other, leading to unnecessary friction and wear.
Secondly, the rolling elements are restrained in some alignment while using the bearing device, which controls the axes of movement. This alignment reduces friction and improves the bearing’s working capability.
Lastly, the material and design of the cage also matter a lot. The materials used for the cage are, however, light but strong with the likes of steel, brass, or engineered plastics. These materials aid in enhancing the weight of the bearing while precisely ensuring wear resistance except during very high speeds or heavyweight usage.
All in all, the cage assists in lessening the friction by (1) providing structure for the needle spacing, (2) achieving accurate alignment of the elements for the needle, and (3) selecting materials that are expected to assist wear and use in high-use scenarios. All these factors, if the cage was absent, would cause a very low efficiency in the system due to more wear of the bearings, leading to multiple problems.
Impact of Radial Load on Friction
Radial Load is vital in the smart bearing as it has a profound impact on the frictional behavior of the bearing, hence it is necessary to design and use the bearing while taking into account its effects. We will provide below the principal parameters which explain this dependence:
- Magnitude of the Radial Load
Radial Loads affect the amount of deformation imposed on the rolling elements in relation to raceway friction. Due to increased radial load, the deformation and contact area may be relatively high hence larger friction is expected. On the contrary, intermediate loading is required to stabilize the rolled elements and disable the slippage effect.
- Dynamic Load Rating (C)
Every bearing has its own dynamic load rating which specifies the maximum radial load that it is able to bear in continuous operations. It is within this area that constant friction is experienced but without the excess of wear or generation of heat.
- Surface Finish and Material Properties
The nature of the contact surfaces is frictional, so their quality is of great significance. Leveled or smoothed surfaces tend to lower the resistant fabric, while the low coefficient of friction materials such as steel or ceramic enable radial load variations to be performed efficiently.
- Lubrication Efficiency
As the radial load goes higher, lubrication becomes ever more important. Increased loads may push away the lubricants or disturb the lubrication film, resulting in increased levels of friction due to the component parts grinding against each other. Using grease or oil of proper viscosity ensures smooth rotation of machinery.
- Bearing Clearance
Under the influence of a radial load, the internal clearance of a bearing may change. Low clearances at high loads may cause high contact forces and high friction, while a high clearance may cause instability. Choosing the appropriate clearance for the given loading conditions optimizes the performance of the bearing.
The impact of radial load friction can indeed be managed efficiently, thereby facilitating longer bearing life, minimizing energy losses, and increasing overall system efficiency. This is made possible by taking into consideration all parameters and ensuring the bearing is operated within its designated parameters.
Friction Comparison: Needle Bearing vs Ball Bearing
In my encounters with needle bearings and ball bearings, the selection process has been mostly need-based as the two are quite different in their design and application. For instance, when using needle bearings, which are space-saving in their construction, the high working tolerances can be greatly exceeded even in small dimensions because of their high load-carrying capacity, but the radial load is efficient as well. Furthermore, a large area can be constructed using ball bearings, which are low in friction and allow for greater rotation speed when high precision or axial loads are applied. In my opinion, the ease of operation geometry of the assembled parts is the determinant factor that balances the range of applicable operational efficiency zones, load requirements, and available space. All of them are quite complex in design and possess great capability when applied in the right geometry.
When should you use Needle Roller and Cage Assemblies?
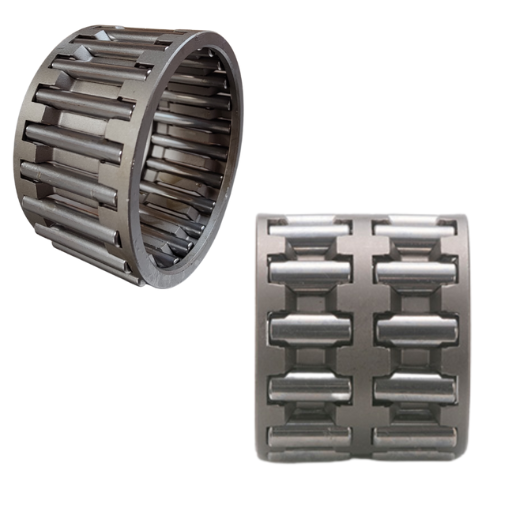

When size restriction is a key requirement, such as in power tools or car gearboxes, and even high radial loads are required to be taken, then needle roller and cage assembly becomes the best option because it provides excellent rendimiento. They provide a load capacity of small axial dimensions but maintain optimal movement. Additionally, their construction allows for the reduction of friction and thus makes their use reliable in harsh environments, making them suitable for high speeds.
Benefits of Using Needle Roller and Cage Assemblies
Based on my industrial experience, I can state that needle roller and cage assemblies are critical for achieving superior performance in strenuous applications. These assemblies excel in that they are compact whilst having great load-carrying capabilities. Their design provides a very low coefficient of friction which improves efficiency and minimizes wear and tear, resulting in greater reliability under high speeds. Moreover, they are designed with accuracy, which enhances smooth motion and depends on the smooth functioning of machinery, which varies from auto parts to industry machinery.
High-Speed Applications for Needle Bearings
High-end Engineering and Advanced Performance make needle bearings among the best choose for high-speed devices, this statement I can quite confidently affirm. Let me explain the respective parameters in more detail why needle bearings excel in such harsh conditions:
- Load-Bearing Capacity –Bearings called “Needles” have been compacted so they can manage decent axial and radial loads. This is important in applications that have a need for a high speed of operation and require maintaining structure under load.
- Low Friction Levels –Because turning pieces do not touch each other hard, moving parts have low friction, which has a direct effect on efficiency and the amount of heat generated. Reduced friction improves the bearing life and enables high-speed operation.
- Durability –Needle bearings are made from high-quality materials, and as a result of this, they have remarkable durability. These bearings can be subjected to high speeds and cannot fail or get damaged due to wear.
- Compact Design –
Needle bearings can be easily incorporated into designs that require a compact bearing because of its slim profile. This small size enables designs that are not heavy while retaining great functionality.
- Precision Engineering –
Since needles are engineered with high precision, they tend to work great when fitted. This reliability is essential in areas like the automobile sector, where components need to function optimally at high speeds.
Ultimately, microminiaturized needle bearings are specially made for high rotational speeds and, therefore, can be applied in a wide variety of cases. Such adaptable designs, together with low weight and exact measurements, guarantee the efficient operation of machinery in the complex world of contemporary industry and automotive technology.
Limitations of Needle Roller and Cage Assemblies
Needle roller and cage assemblies have their own set of disadvantages, even though they have wide-ranging advantages. These are very practical due to their compact profiles; however, they are very misaligned and sensitive, which causes early wear and reduced efficiency. Also, in order to work efficiently, these are required to be lubricated properly because a lack of these would cause high friction and even failure. Certainly one of the best engineering solutions, but their load/grip capacity pales in comparison to the more or less larger types, especially for heavy load applications. Last but not the least, there Installation and assembly have to be both done properly, even a single sandwich grease means loss of reliability and a shortened lifespan.
What Are the Different Bearing Types?

I’ve encountered a range of bearing kinds, from ball bearings, which are well renowned for their versatility and efficiency, to needle bearings, which are most suitable for small and tightly constrained areas. It all comes down to the intended application of the machine, for instance the industrial needle bearings are better when there is an extreme load required, while the rotating types of the ball bearings are better suited for radial and axial applications. However, if the procedure is of a high_bp, then it would be better to go for angular contact bearings; otherwise, if the goal is to take axial loads, then the thrust bearings will fit perfectly. It’s a matter of determining the intended motion and how much compact gear you’re willing to abide by.
Comparison Between Ball Bearing and Needle Bearing
There are differences in the ball bearing and the needle bearing mainly in the application and also in the design. Ball bearings employ the use of spherical rolling components, which simplifies dealing with both radial and axial type forces, though at moderate speed but with high roughness. On the other hand, needle bearings use cylindrical rollers that are long and thin, which allows them to carry larger radial forces in applications where space is restricted. Even though ball bearings are multipurpose and used in multiple industries, needle bearings are suitable for environments with high radial forces and limited space for installation.
Overview of Rolling Bearing Categories
Based on my experience in the industry, rolling bearings can be divided into several categories, which have particular purposes and conditions of use. These comprise ball bearings, which are considerably adaptable and work in cases of different load types; roller bearings, which provide strong bearing support for heavy work; and needle bearings, which are compact and capable of high radial load. Moreover, there are several other special types, for example, tapered roller bearings, spherical roller bearings, and thrust bearings, that aim at specific needs such as orientation, vibration control, or a single-direction load. It is very important to comprehend all of these in order to, in the end, bear in mind which bearing should be used in a particular mechanical system in order to obtain better performance, efficiency, and service life.
Specific Uses for Radial Needle Roller Bearings
Radial needle roller bearings are used in radial needle applications, with a clean application and high loads ear. This is due to having compact designs while sustaining high radial loads which makes them suitable for automotive transmissions, compressors, and gearboxes. They are also commonly used in industrial machinery, such as robotics and textile machines. Due to their ability to work in low, confined spaces, they can be used in the mix to achieve greater performance in harsh mechanical environments.
How Do Needle Bearings Handle Radial and Axial Loads?
Absolutely! Based on my experience, there exists a variant of roller bearings called needle bearings. These bearings are specially made in such a way that they can support radial and axial loads effectively. Let us examine their performance in each case:
- Radial Loads: Needle bearings perform excellently in radial loads because of needle rollers. The small cylindrical rolls bear the load across a greater surface area than ball bearings. Their compact structure increases the radial load capacity of the needle scoop simultaneously making it highly effective. The key parameters here include:
- Roller Length-to-Diameter Ratio: The higher the ratio, the more the load is distributed and the capacity is enhanced.
- Material Strength: The use of high-grade steel or alloys guarantees that they are hard-wearing and do not deform under strong mechanical forces.
- Lubrication Quality: Appropriate lubrication greatly reduces friction and heat and thus increases performance under static or rolling loads.
- Axial Loads: Needle bearings are not designed for axial loads; however, if some measure, including the use of thrust washers or other combined bearing arrangements, is adopted, then needle bearings are able to withstand mild axial loads. This works especially well in systems where minimal axial displacement is required. Key performance factors are:
- Axial Support Design: The incorporation of thrust cages or washers increases the support design axial load capacity.
- Alignment Precision: The correct positioning of the shaft bearings minimizes the stresses endured by the bearing, thus allowing it to function properly.
- Load Distribution: Even the application of load on the bearing prevents the bearing from excessive wear or damage due to the application of non-uniform forces.
To conclude, needle bearings are versatile, which means they are capable of bearing radial and axial loads due to proper engineering and the correct application. The correct application of these parameters ensures that the efficiency and durability of the bearings are maximized even in challenging environments.
Understanding Radial Load in Needle Bearings
Customer feedback is key to progress, and so understands the engineering at ung engineerings, as they say from my experience in the field, understanding radial load in needle bearings is captured in – how these components are figured in such a way that they can withstand high forces within relatively small spaces. Radial load – is the force that is applied perpendicular to the axis of the bearing, and needle bearings are able to bear this kind of force because they have long rollers and a wider load-carrying capability. Bearing radial loads especially benefit from the proper lubrication and shimming to maintain their geometric positions. Mechanical components are functioning and do not cease to develop. I have repeatedly witnessed how these details affect the bearing resource and the machine quite efficiently over the years.
Performance under Axial Load Conditions
Contrarily to the sideload, the axial load is positioned parallel to the center of the bearing. Simple thrust washers or combined needle-thrust bearings can utilize light axial loads and are able to be partnered with needle bearings. Although much greater forces would require specialized equipment in order to avoid wear and destruction, axial bones would be quite helpful in lowering significant weight. It is then preferable to use appropriate equipment and alignment; otherwise, it is most likely to fail.
Design Features for Managing Load than Ball Bearings
Needle bearings have greater load-bearing capacity than ball bearings, and this is due to their design. Thanks to its long cylindrical rollers, the needle bearing produces a greater contact area, thereby distributing load better and alleviating the stress and wear on individual sites. Such a construction allows a greater load-carrying capacity to radial forces in particular. Also, needle bearings’ low profile makes them suitable for numerous applications where space is at a premium, but performance still counts. Proper lubrication and the use of appropriate materials also support better load management for long periods of time.
Reference
- SKF – Needle Roller Bearings
- ISKBearing – The Comprehensive Guide to Needle Roller Bearings
- Universal Bearings – A Guide to Needle Bearings
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is a needle roller bearing, and how does it differ from other types of bearings?
A: A needle roller bearing is a type of bearing that uses long, thin cylindrical rollers resembling needles. It differs from other types of bearings, such as deep groove ball bearings or angular contact ball bearings, in its ability to handle heavy radial loads in compact spaces. Needle roller bearings are particularly useful in applications where radial space is limited but high load capacity is required.
Q: What are the main components of a needle roller bearing?
A: The main components of a needle roller bearing include the needle rollers, an outer ring (which may be absent in some designs), and often a roller cage to keep the rollers properly spaced. Some types, like drawn cup needle roller bearings, feature a thin-walled outer ring. The bearing steel used for these components is specially chosen for durability and performance.
Q: What types of needle roller bearings are available?
A: Several types of needle roller bearings are available, including drawn cup needle roller bearings, thrust needle roller bearings, and needle roller and cage assemblies. Each type is designed for specific applications and load conditions. Thrust needle bearings, for example, are particularly suited for axial loads, while radial needle roller bearings excel at handling radial loads.
Q: How do needle roller bearings compare to ball bearings in terms of load capacity?
A: Needle roller bearings can generally carry higher loads than ball bearings of similar size. This is because the linear contact between the rollers and the races distributes the load over a larger area compared to the point contact in ball bearings. However, ball bearings are designed to handle both radial and axial loads more effectively in certain applications.
Q: What are the advantages of using needle roller bearings?
A: Needle roller bearings offer several advantages, including high load capacity, compact design, low friction, and the ability to operate at high speeds. They are particularly useful in applications where space is limited but bearing load requirements are high. These bearings are used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery.
Q: How should needle roller bearings be maintained?
A: Proper maintenance of needle roller bearings involves regular lubrication, cleanliness, and periodic inspection. The bearing must be kept free from contaminants and lubricated according to the manufacturer’s specifications. It’s important to check for wear, ensure proper alignment, and replace bearings when necessary to maintain optimal performance and prevent equipment failure.
Q: Can needle roller bearings handle both radial and axial loads?
A: While needle roller bearings excel at handling radial loads, their ability to manage axial loads depends on the specific design. Standard radial needle roller bearings are not suited for significant axial loads. However, thrust needle roller bearings are specifically designed to handle axial loads. For applications requiring both radial and axial load capacity, combined needle roller bearings or other bearing types may be more suitable.
Q: What factors should be considered when selecting a needle roller bearing?
A: When selecting a needle roller bearing, consider factors such as load requirements (both radial and axial), operating speed, space constraints, lubrication needs, and environmental conditions. The specific application, whether it involves rotary or oscillating motion, also plays a crucial role. Consulting with bearing manufacturers or engineers can help ensure the right type of needle roller bearing is chosen for optimal performance and longevity.
