Bearings are of course very important car parts as they help in the smooth and stable movement of the vehicle, more like the foundation of any structure. But riding on a defective wheel bearing can compromise your safety and the performance of the vehicle itself. So, determining the health of the wheel bearing is a very important step in preventing further damage or expensive repairs. This guide will help set forward a set of boundaries so that one is able to locate the signs of a defective wheel bearing and then understand the function it does in the vehicle, after which simple methods of diagnosis can be employed to locate the problem. So, whether you are a die-hard car lover or a beginner in vehicle service, read the article since it will give you an understanding of performing basic vehicle diagnosis of this ever-common issue.
What are the wheel-bearing symptoms?
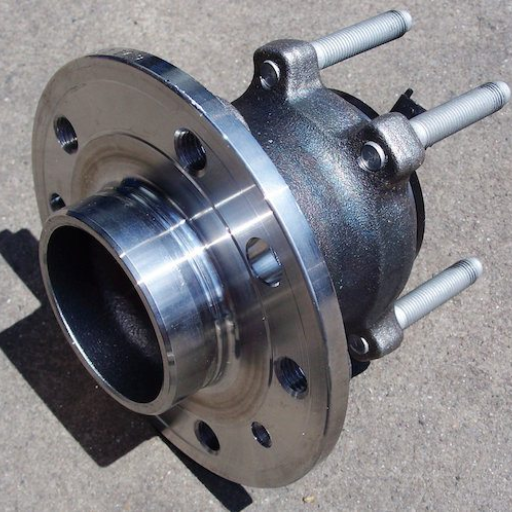

One of the crucial components of a vehicle is the wheel bearing, and as normal with every machine, at some point, the wheel bearing will begin to fail and exhibit some indications. The wheel’s hub bearing is known to cause strange sounds, like (but not limited to) thumping, grinding, or humming, and these strange sounds can be Loud when the vehicle accelerates or turns. Other indicators include steering vibrations, unbalanced feeling in the vehicle, and the more severe case is the vehicle’s tires display uneven wear and tear and excessive loosening and wobbling of the rear wheel hub assembly. It is best to take note of warning signs early in order to secure the safety as well as performance of the vehicle.
How does a bad wheel bearing make noise?
A broken bearing, according to what I have experienced, usually starts off as a low-pitched growl or rumble that changes with increasing speed. It usually starts off as a low sound, but as the bearing gets worse, it increases in severity. When the car turns, the load distributes onto the bearing and subsequently leads to a change in noise. Sometimes in its case, one may also hear a whine or grinding sound particularly if the bearing is relatively bad. These are nothing but the result of friction – when the metal rubs against each other without any lubrication or when there is wear or damage inside the bearing.
What sounds indicate a bearing is bad?
When it comes to identifying a bad bearing, there are a few distinct sounds you should listen for, and I’ll break these down for you in detail:
- Humming or Rumbling Noise –One of the earliest sounds to appear and arguably one of the most prevalent. When there are bad bearings, a low-pitched hum or rumble may occur, which may be felt more efficiently as your speed picks up. This happens because of the wear that has caused uneven rotation of the bearing.
- Grinding or Metal-on-Metal Noise –Considering this idle Kine Mazda engineer, it sounds like if the bearing has some damage, then a grinding noise may come out and would be rather rough. In most cases, this means that parts of the bearing are nearly worn out or too much lubricant is not provided between the components, which causes them to touch each other directly.
- High-Pitched Whine –A sharp whining noise is very common when there is tension on a specific bearing. Over-mounting, inadequately fixing, or excessive friction can cause this to happen.
- Changes During Turning – There can be a change in noise while turning. This change may be ample to say that one bearing is faulty. This change occurs because of some force applied on the bearing, but that force is not equal based on the load bushed onto the bearing.
- Clicking or Popping Noises – Though seldom, sometimes clicking or popping noises may be heard,d particularly during acceleration and deceleration due to fracture in the internal bearings.
Every single one of these sounds corresponds to certain problems in the bearing, like lubrication failure, mechanical abrasion, incorrect position, or some disfigurement. Listening to these noises and noting the times they appear and when the issues occur will help solve the problem in the shortest time and preserve the safety and integrity of your automobile.
Does the noise get louder when you steer?
unusual sounds that rise when you begin turning the wheel are a great sign that there are issues mechanical issues with the wheel bearing. The muff economist who specializes in engineering explains that when there is a broken wheel bearing, and the car is driven in the opposite direction to the broken wheel bearing, the broken cement wheel bearing becomes even louder. In other words, if the noise increases in the left-hand turn, then the right wheel bearing is defective. This is attributable to the maneuver putting greater stress on the Broken component. Recognizing this pattern in its early stages can help prevent the problem from escalating.
How can you tell which wheel bearing is failing?
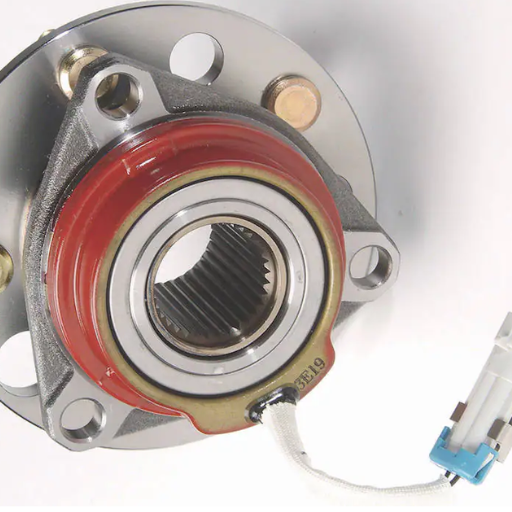

Watch the noise while driving so as to find out which wheel bearing is failing. A faulty wheel bearing generally causes a humming noise or some grinding or growling sound, which varies with a change in vehicle speed. Carry out a turning test – the noise during a turn gets louder, and that is where the failing bearing is, which is on the opposite side of the increased load. Also, search for excessive play, for example, by lifting the vehicle and checking the wheel for looseness or rough rotation by hand.
Steps to identify a bad wheel bearing
Bad wheel-bearing diagnosis, is an incremental process involving a few simple tasks. To begin with, check for any strange sounds while driving—most of the time, a defective wheel bearing sounds like a grinding or growling sound that is likely to get worse as the speed of the vehicle increases. Then, turn the car using one side only, and during the turn, listen if the car is making louder noise than usual, this almost always implies that the opposite side bearing is getting bad. Lastly, let’s raise the car on a jack and check the wheel. Try to shake the wheel if there is any free play, try to manually spin it, and check if there is any uneven spinning. If this is the case and if the play is excessive, it’s likely that the wheel bearing is defective. These steps are crucial for precise evaluation and effective service.
How to determine which wheel is affected
To find out the wheel with the faulted bearing, do the following systematically, which will allow for an easy and correct diagnosis:
- Listen for Noise While Driving
When a wheel bearing goes bad, it has a specific sound — either a rumbling or grinding sound all the time. When you hear it, try to gauge which side of the car the sound is coming from. Sometimes, it may be the case that increasing the car’s speed makes the sound more loud, and hence, you are able to figure out the faulty wheel.
- Conduct a Turning Test
Steer the wheel to the sides but slowly. A change in position leads to a shift in the load equilibrium of the vehicle. If the sound was increasing as you made a turn to the right, then the bearing of the left side wheel is probably the responsible one. On the other hand, more noise when the left side turn is made is most probably a problem with the right side bearing.
- Perform a Physical Inspection
Make sure the vehicle is in place by using a jack to hold it still. From there, make sure you follow one wheel at a time. For example, you can try to push the wheel in both vertical and horizontal directions. If you notice it is rather loose, then the chances of it being a failed bearing are high. Next, to confirm your inclination, try moving the wheel with your hand whilst also checking for any abrupt changes, friction, or grinding.
- Observe Temperature Differences
After driving for some time, try to take a closer look on the heat of the wheels to measure (ideally get an infrared thermometer and measure it). There is a part of the bearing that is busted; it would lead to an increase in friction, hence causing the wheels to get hotter than usual.
- Check ABS Sensor Data
ABS systems can be useful in diagnosing vehicle problems if fitted to your vehicle. Open the OBD-II scanner to look for any readings that might indicate a wheel balance or error of a particular wheel.
With diagnostics for autos, getting the job done is significantly easier. All you require is a clear vision of which wheel has an issue, and exploring the parameters step by step can aid in figuring that out immensely.
Using a steering wheel test to diagnose
The steering wheel test, , has helped me with the diagnostic of all sorts of issues with the automobile. Here is the way this test works: With a sub-moderate speed on a straight and flat road, observe how the steering wheel works for you. Does it show a tendency to pull towards one side and not rest in the middle? If yes, there could be problems with the alignment of the wheels, uneven pressure on the tires, or a brake caliper sticking, among other things. Furthermore, any vibration through the steering wheel during braking can be associated with warped rotors or unbalanced wheels. While it may not be perfect technology, assessing these particular details should allow me to make some conclusions as to the underlying mechanical problems.
What causes a bad wheel bearing?
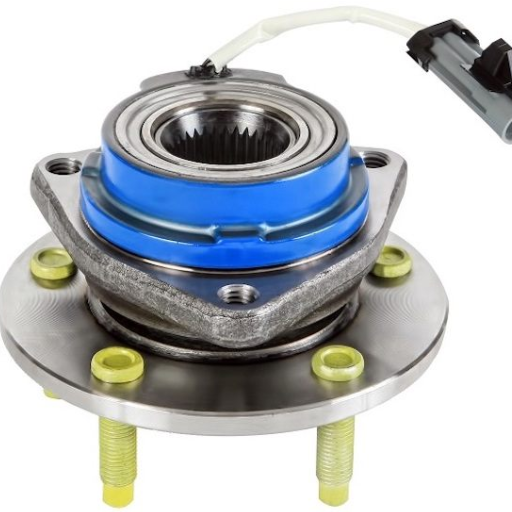

It is not uncommon for a wheel bearing to wear out over time, especially when being driven roughly. There are several participants that serve to assist with this, including low lubrication, dirt or water infiltrating the bearing, low-quality stuff, or high pressure and impacts, say from potholes or curbs. All of these processes ruin the bearing structure and, in turn, produce noise and vibration and reduce the overall efficacy of the vehicle. Sometimes, just performing maintenance and being on the lookout for abnormalities that could indicate a fault will go a long way.
Common reasons a wheel bearing is bad
Based on my observation in the industry, the most common issues faced while replacing a wheel bearing are primarily due to environmental factors and negligence. For example, there are instances where bearings lose lubrication instead of having too much, which results in overheating and eventually failing to function. Also, bearings corrode surfaces due to being contaminated by water, road salt, or dirt, thereby increasing the rate of wear and tear. Furthermore, it is also true that bearings manufactured out of poor materials generally do not possess the strength to last through extended amounts of usage. Drawing from my experience, I always highlight the significance of protecting bearings from suffering a heavy blow from hitting a curb or potholes, as such impacts irreversibly damage the bearing. Regular checks and early remedy of issues are major factors against wheel bearing’s wear and tear.
How lubrication issues lead to failure
Lack of lubrication causes heat and friction to build up in the wheel bearing, which disrupts the balance of the internal parts. Likewise, the internal components of a bearing tend to wear out in the absence of adequate lubrication, which could lead to the elements cracking, pitting, or freezing completely. A dirty or insufficient lubricant makes the problem worse as it brings abrasive particles that ruin the bearing surfaces, which hastens failure.
Impact of hub and axle problems
Hub and axle issues greatly affect the working of wheel bearings, and from my understanding of the industry, this is a common occurrence. If the hub or axle gets damaged or misaligned, then too much stress is applied to the bearing, which increases the chances of the bearing failing or wear and tear. Out-of-tolerance components put additional stress, which leads to friction and heat because these components make it more difficult for the bearing to rotate. Hub imbalance and axle imbalance also contribute as both cause unwanted vibrations, which take a toll on the structural integrity of the bearing. The aforementioned problems all need to be solved promptly in order to ensure that the system remains reliable and has a significant lifespan.
How does a failing wheel bearing affect driving?
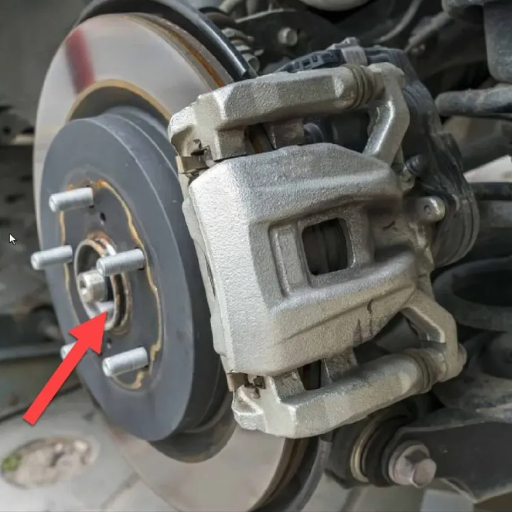

In a way, the simplicity of driving dismisses the critical bearings in the vehicle, but ignoring a failing wheel bearing should never be an option. Allow me to break it down into key points so it’s clear why this component is so critical:
- Noise Levels
An unusual noise, particularly humming, grinding, or roaring sounds emanating from the wheel bearing, indicates that it is close to failure. The noises will be especially prominent during acceleration. The cau
se of this begins with the wheel bearing itself, which does not function smoothly anymore due to contact with metal components in inappropriate locations.
- Vibration and Steering Instability
If a wheel bearing becomes faulty, the vehicle will experience increased vibration felt through the steering wheel and/or the entire car. It can become even more pronounced when taking a turn due to a greater load placed on the broken wheel bearing. The degree of freedom for the shaft can be excessive, making the steering feel ‘loose’ and unreliable, a serious safety issue.
- Uneven Tire Wear
As the motor rotates the wheel, the bearings that help to support this motion help to eliminate wobble, which can cause the tires to wear out quickly. Failure of the bearing will lead to the tire wobbling and performing unevenly, resulting in short tire life. A wheel bearing in the process of failing leads to increased wear and tear on the tires.
- Overheating Risks
Excess friction is caused by overheating bearing parts that are not moving, and if proper temperature control is not maintained and overheating becomes higher than what the system can withstand, surrounding components like axles, brakes, etc, will be damaged, which will substantially increase repair expenditures and lead to roadside breakdown.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency deteriorates, too, as the added friction and uneven wheel rotations are present. The engine will have to work overtime to keep you moving, and as a result, you will burn an unusually high amount of fuel.
- Braking Performance Impairment
Another issue too is that the faulty wheel bearing interferes with the brake system as well. Considering that the hub bearing is integrated into the hub assembly, its malfunction can cause problems such as pulsating brakes or even slow down the braking response, which can be hazardous during any emergency.
Solving these issues as soon as you start noticing signs is crucial in relieving the damage and excessive costs associated with repairs. Keeping an eye on wheel bearings could easily be helpful as long as it is coupled with regular maintenance checks.
Signs when the front wheel bearings are the culprit
In my perspective, there are some glaring signs of malfunctioning wheel bearings and one of them is the sound that is produced, such as groans or grindings. As the vehicle accelerates, these sounds become more prominent and further increase when turning. The front wheel bearings being defective can lead to aching vibrations in the steering wheel which can be methodologically problematic while on the road. Moreover, when the front wheel bearings start to fail, the uneven treadwear and pulling to one side can also be signs of it. These are all signs that need to be monitored closely because they can prevent not just extensive repairs but also ensure the car runs smoothly without any problems.
What happens if the bearing is the culprit?
If the problem is with the bearing, it can result in a range of repercussions. Due to the increase in deterioration of the bearing, there will also be a rise in excessive friction, which creates heat that has the potential to even damage surrounding parts such as the hub or axle. If a bearing starts to fail, it may also start to affect the way the car handles, meaning it may be able to wobble or, in some extreme scenarios, not even turn. This not only puts your life in danger but also means that chances of further expensive repairs increase. This need not be expressed; it is common knowledge that a damaged bearing should be replaced as quickly as possible to keep your car intact and working smoothly.
How do you fix a wheel bearing problem?
In order to bring a solution to a wheel bearing problem, the first step is to change the damaged wheel bearing. In this case, it is necessary to lift the car, take off the wheel, brake assembly, and, in some cases, the hub to get access to the bearing. Some specialized tools may be necessary to press out the faulty bearing and to press in the replacement one. After that, the parts must be put back together with whatever has been retorqued according to the specifications. If you lack experience, it’s advisable to hire a professional mechanic since improper installation can further damage the part or put the safety at risk.
When to replace a worn bearing
if you must replace your bearing, do so as soon as you hear a warning noise. This warning noise can be in the form of humming noises, grinding, metallic sounds, being able to wiggle the wheel, or even uneven tire wear. If these warning signs are ignored, the damage could be severe and put your vehicle and its driver’s safety at risk. It’s these issues that I always advise my clients to deal with at once and not delay them because a timely repair could avoid a blockage and keep the vehicle in good working order.
How to jack up the wheel for inspection
In order to check the wheel, I first check if the parking brake is engaged as well as if the vehicle is on flat and stable ground. Then, I place the wheel chocks on the tires on the opposite side of the one being inspected so that it does not move. After that I make use of a jack that fits the car and find the spot recommended by the manufacturer close to the wheel. Gradually raising the car, I check if the wheel is off the ground, and then I keep a jack stand under the vehicle for maximum safety. You will want to make sure to never use the jack alone to support the car. Due to the wheel being raised up and secured, I am now able to check in more detail without any restrictions.
Steps to change a faulty wheel bearing
This is a process that can be carried out in a stepwise fashion once the answer has been found to change a broken wheel bearing, as it may seem challenging. Make sure to follow these steps carefully:
- Ensure Safety First
- To begin, your vehicle should be on level ground, and the parking brake should be set.
- It’s a good idea to place wheel chocks on opposite wheels to stop the vehicle from rolling.
- Gather Necessary Tools
- You would need a breaker bar, car jack, jack stands, a few socket sets, a donut wrench, a torque wrench, a hammer, and bearing tools like a ‘press’ or ‘puller’ if you have any.
- Jack Up the Vehicle and Remove the Wheel
-
It’s safe enough to remove the lug nuts with a wrench, and this will allow you to detach the wheel to expose the brake and hub assembly.
- Detach the Brake Caliper and Rotor
- The first step in removing a brake caliper involves unbolting the mounting bolts. Hang it up using a zip tie or bungee cord to avoid tensioning the brake lines.
- The next step is to slide the rotor off the hub assembly; if the rotor seems stuck, consider gently tapping it with a rubber mallet.
- Access the Wheel Bearing
- Depending on the model of your vehicle, begin loosening the axle nut using a breaker bar or an impact wrench. In the case that the nut is extremely tight do not fully lift the car prior.
- Remove any wires, including sensor wires attached to the hub, that should interfere with bearing removal.
- Remove the Faulty Bearing
- The bearing or hub assembly must be bolted and unbolted prior. Depending on the vehicle mode,l the faulty bearing could be a press-fit bearing or one that is mounted on the hub assembly.
- Remove the old bearing using a specialized removing tool or bearing press. Be very careful as misplaced striking can damage crucial components.
- Install the New Bearing
- The new bearing will be pressed into the hub or assembly using a bearing press. Ensure that it is fitted in place firmly without over-tightening it.
-
The last step is to bolt the hub assembly or bearing to the vehicle.
You can avoid mistakes and bear a full wheel bearing replacement by following each step carefully. Always be on the safe side; if you’re ever uncertain about a task go seek the guidance of a certified mechanic.
Reference
- Kelley Blue Book: How Do I Know if I Need a Replacement?
- SKF Vehicle Aftermarket: Symptoms & Signs of a Bad Wheel Bearing
- Free ASE Study Guides: Wheel Bearing Diagnosis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the common signs of a bad wheel bearing?
A: Common signs of a bad wheel bearing include a humming noise, grinding noise, or a rumbling sound while driving. These noises may get louder when turning left or right. If the noise goes away when turning in one direction, it could indicate a bad wheel bearing on the opposite side.
Q: How can I determine if the noise is from a bad wheel bearing or a bad cv joint?
A: A bad wheel bearing typically causes a humming noise that changes with wheel speed, while a bad cv joint often produces a clicking or popping noise during turns. If the noise changes or remains constant with speed, it is more likely related to the wheel bearing.
Q: How can I identify if the bad wheel bearing is on the left or right side?
A: When a wheel bearing is probably bad, the noise usually increases when turning away from the bad side. For example, if you are turning left and the noise goes away, the left wheel bearing may be the culprit.
Q: Is there a difference between diagnosing a front or back wheel bearing issue?
A: Yes, diagnosing a front or rear wheel bearing issue involves similar steps, but the location of the noise (coming from the front or rear) can help pinpoint which wheel has one. Whether it’s the front axle or rear axle, the same principles apply.
Q: Can I tell if a wheel bearing is bad when spinning the wheel?
A: Yes, you can allow the wheel to spin freely by lifting the vehicle and manually turning the wheel. Listen for unusual noises or resistance. If the wheel spins roughly or produces a grinding noise, it might indicate a bad wheel bearing.
Q: What speeds (mph) typically reveal wheel bearing issues?
A: Wheel bearing issues often become noticeable at speeds above 30 mph. The humming or grinding noise may increase with speed, making it easier to diagnose at higher mph.
Q: How do roller bearings affect wheel bearing performance?
A: Roller bearings are designed to reduce friction and ensure smooth operation. A lack of a constant source of lubrication or damage can lead to increased friction, causing noise and indicating a bad wheel bearing.
Q: What should I do if I suspect a bad wheel bearing on the driver’s side?
A: If you suspect a bad wheel bearing on the driver’s side, please consider having it inspected by a professional mechanic. Diagnosing the exact issue and replacing the bad bearing is crucial for safe driving.
Q: Can a bad wheel bearing affect both the front and rear wheels?
A: Yes, a bad wheel bearing can occur on either the front or rear wheels. Each wheel drive system, whether it’s a four-wheel or two-wheel drive, requires functioning bearings per wheel for optimal performance
