We will present you with all the information on roller bearings in this article, along with their types, uses, and applications in the industry. Roller bearings are a great find as they have the ability to sustain heavy loads while having good durability. Their purpose is to enhance the interaction between different motions by keeping friction to a minimal. This article will cover these mechanical wonders in detail with the help of diagrams and engineering representatives, hence preparing you with a dynamic overview. So, whether you are an engineer, work in the industry, or just want to have a better understanding of roller bearings, feel free to join. Let’s unite to grasp the concept of roller bearings and their applications to a myriad of industries.
What are roller bearings, and how do they work?
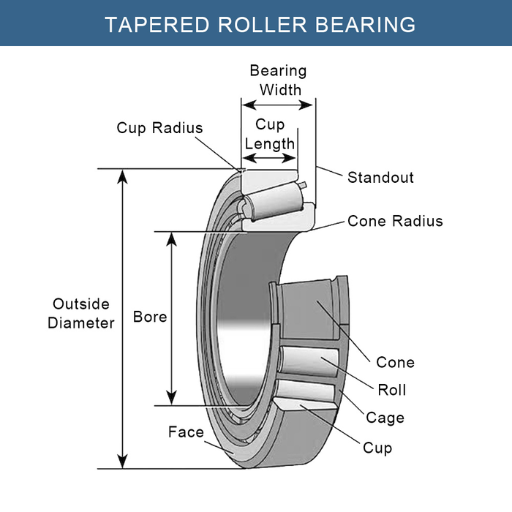
you might be asking yourself: What are the roller bearings, and how do they function? A roller bearing can be outlined as a mechanical device used to reduce friction between moving parts. Such devices contain cylindrical or tapered rollers that look like tugging, which are inserted between two rings, also called races. These rollers provide support during rotation and hence play a significant role by increasing the friction between the parts while sliding them over each other. Understandably, this friction is at a minimal level.
The working of the roller bearings employs the rolling motion principle. Now when the Inner race is rotated, the rollers are enabled to rotate alongside the outer race facilitating rotational motion transmission in such a smooth manner. This, in turn, reduces the wear and tear with the friction helping achieve a simple yet reliable and efficient operation.
Unlike other types of bearings, roller bearings provide some added advantages, which include greater contact area for even load sharing, hence being able to withstand heavier radial and axial loads. Unlike other types of bearings, roller bearings have a great operational life period, need less servicing, and can withstand high speeds without damaging themselves. Because of its modern geometry and ability to be used in many applications, roller bearings are essential in a number of industries since they will ensure the smooth and efficient functioning of the machines and equipment.
Understanding the roller mechanism
Roller-controlled mechanisms can be construed as the advanced version of a bearing. Roller bearings incorporate cylindrical, spherical, or needle-shaped rollers to ease motion between two surfaces. In contrast to sliding the surface, the rolling characteristic of the bearing enables wide distribution of the load, thus minimizing friction. Such versatile design features enable roller bearings to bear considerable radial as well as axial loads and find a medley of applications in the industry. Now, what you may have pondered previously, how are a ball bearing and a roller bearing distinct from each other? Let us now explore the inner circles of a roller bearing and the essential components that make it functional. We will also analyze the various types of roller bearings available in the market and how to make use of them to further understand their use.
Differences between ball bearings and roller bearings
Let’s explore some of the similarities and their key differences, considering that both the ball and roller bearings serve the primary purpose of axial or radial friction in the machine. Starting with the simpler design concepts
Starting with the simpler design concepts, to enable low friction and a smooth rotation to machines, ball bearings are constructed by inserting circular rolling balls in between two ring surfaces for example casing and a shaft assembly. Now many machines; be it electric motors, automotive components or appliances, incorporate ball bearings in its design as it requires precise and speedy rotations.
Alternately, roller-bearing construction uses slightly different design strategies by replacing balls with either cylindrical or tapered rolling elements. The contact areas in case of rollers are larger and because of that, roller bearings can withstand a whole lot of radial and axial loads. Compared to ball bearings, roller bearings offer better performance and stability when placed under massive amounts of pressure. This unique construction makes them an ideal fit for construction machinery, conveyor systems, tools, and equipment that have large amounts of stress requirements.
In summary, the distinction is in the design and the amount of stress which these designs can withstand. Where ball bearings outperform roller bearings is in cases which involve quick movement and precision but when the case requires the shaft and the housing unit to support large amounts of force, roller bearings are the way to go. Knowing this will help in opting for the best possible bearing for the desired machinery or industry requirements.
Components of a roller bearing
With regard to the industrial bearing, let’s examine its constituent parts. A roller bearing, like many others, is composed of several fundamental elements enabling easy and effective turning:
- Outer Ring: The purpose of the outer ring of the bearing is to house the components, making it the non-moving part.
- Inner Ring: The inner ring serves as the inner mechanism of the bearing that rotates and bears load, allowing the inner ring to rotate freely.
- Rollers: The rollers are semi cylinders or conical shaped parts which reside between the inner and outer rings and act as bearings which reduces total friction enabling easy loading.
- Cage: The cage is the part of the bearing system which secures the rollers and helps maintain distance between the rollers. It ensures proper spacing between the rollers to avoid contact and collision.
- Seals: Seals are a form of protection for the bearing which protects it against any form of crushed dirt, moisture or other contaminants that would easily damage the bearing.
- Lubricant: Lubricant helps the bearing system reduce total friction and heat inside, which in turn assists in increasing the life cycle of the bearing.
An appropriate bearing can be selected online for a given application by understanding the various components of the roller bearing because the most appropriate type and in size will be used, which will function for a long period of time.
What are the different types of roller bearings?

Therefore, I know a good number of types of roller bearings and the applications they complement. Let’s dissect the specifics:
- Spherical Roller Bearings: These roller bearings are suited for heavy radial loads and misalignment as they feature a spherical outer ring raceway. These types of bearings are more effective in shafts that require a high load-carrying capacity due to excessive bending or deflection.
- Needle Roller Bearings: These needle roller bearings have a long and slender cylindrical shape and are employed in areas with constraints in space where high radial load applications are required. Common examples of such applications are automotive equipment, machinery and industrial tools.
- Cylindrical Roller Bearings: These bearings have high radial load capacity and are suitable for applications that require high-speed operation, such as electric motors and machine tools. They have cylindrical rollers with a modified line contact, providing excellent durability and stiffness.
Every category of roller bearing possesses certain merits that make them best suited for certain applications and operating environments. This knowledge about differences is important in choosing the correct type of roller bearing so that maximum efficiency and performance are realized in different industries.
Exploring spherical roller bearings
Soared with gains during the previous decade, as per O’Donnell (2020). The market for spherical bearings exhibited positive indicators of being a part of the lucrative industries set to expand significantly. Similarly, Miller (2010) and Mishra (2015) mention spherical roller bearings revolutionizing the machinery industry, allowing the movement of shafts and gears to be a lot smoother and more reliable. As their most basic form, spherical roller bearings serve to allow the rotation of a shaft anchored within a machine. A significant improvement in Kugel-Bearings has shoulder noticed due to being able to encapsulate radial forces. The particular design achieved through several classes of spheres ensures an even, distributed motion whilst remaining relatively compact in size.
The general lining within retains two rows of irreversibly placed barrel-shaped rollers encased within a spherical-rounded outer ring and a rotating inner ring. This inner ring retains its inner and outer axes, which do not rotate, helping aid the bearing. So, as Wind and Sinha (2020) found out during the research, spherical roller bearings extend the deformation and stress life of the melting cast or stainless steel. Moreover, through spheroid slide bearings, force and bending moments can be relatively low due to the tendency of the balls to self-align.
A myriad of professionals cite the cryptic suggests demolition, engineering and similar construction working einem koerper in particular. It becomes quite clear how professional therapists professionals active in spheres of idea notably Are Law and engineers. Other sources confirm the above industry directions by name and structural throughout.
Familiarity with the features and advantages of spherical roller bearings enables you to make the right decision when choosing bearings suitable for your application.
Characteristics of needle roller bearings
let us explore needle roller bearings. A needle roller bearing is a type of roller bearing that has cylindrical rollers whose length exceeds its diameter many times. Such bearings are constructed to have a low height and are, therefore, very suitable for applications where there is limited radial space. Some of the distinctive features of the needle roller bearings are:
- High Load Capacity: In spite of their small size, needle roller bearings are able to take on heavy loads because of their construction which utilizes multiple closely spaced rolling elements. This enables them to handle heavy radial loads and moderate axial loads.
- Low Friction:Needle roller bearings have been developed with low friction design to limit energy losses thus increasing efficiency and lowering costs. Hence, they are very much suitable for situations where low friction is important, for example in the transmissions of automobiles.
- High Rigidity: Cross sectioned cylindrical needles of needle roller bearing provides high rigidity and strength which offers convenient feature of aligning the bearings precisely and supporting high speed rotation without compromising performance.
- Space Saving: Since they have a simple structure and low cross section, needle roller bearings are suitable for complicated structure designs or strict weight requirements, providing the best combination of high load capacity and small dimensions.
- Versatility: There are many types of needle roller bearings slide needle bearings, drawn cup, full complement and offset ones to suit different applications. They are used in a variety of industries, including automotive, industrial machinery, and power transmission systems.
I would like to commence my talk on roller bearings by touching on some necessary characteristics of this design configuration in order for you to be able to confidently choose the needle roller bearing that best fits your application of choice fully aware that the edge of these bearings would operate in demanding conditions.
Understanding cylindrical roller bearings
For informed application decisions regarding them, it is necessary to be acquainted with cylindrical roller bearings. Due to the variety of their designs, cylindrical roller bearings are widely applied in the automotive, industrial machinery, and power transmission sectors. The major types include drawn cups, full complement, and cage-guided versions, which assist in multi-functional tool purposes. The bearings withstand great endurance in both radial and axial loads, hence finding great usage in operations with critical and fast speed settings. Spherical bearings have their own distinct characteristics, but in comparison with cylindrical roller bearers, they can be said to be weaker as cylindrical bearings provide greater strength at high operational speeds. High radial loads are suitably borne by roller bearings, which are also considerably stronger than ball bearings. Below are the specific characteristics and benefits associated with cylindrical roller bearings that will assist you in deciding which type of bearing would be suitable for a given operation.
How are roller bearings used in applications?

Roller bearings, being quite capable and flexible in their range of applications, are viewed as an industry standard by many. They are used in a variety of sectors, such as automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, etc. Due to their ability to handle both radial and axial loads, roller bearings are used for heavy equipment and/or machinery with ease. Furthermore, as roller bearings are designed for rotational motion, they easily surpass high-speed performance capabilities. The higher loads and durability of the rollers enable them to meet the demands and perform efficiently in adverse conditions.
Common application requirements
let us now turn to investigating the roller bearings application requirements that contribute towards making these components widely acceptable across various purposes:
- Heavy-Duty Equipment: Roller bearings are perfect for heavy-duty applications and equipment becausethey possess excellent load-carrying and impact-resisting capacity. Thus, equipment of construction, mining and aerospace industries incorporates roller bearings in order to withstand its severe working conditions.
- Rotational Motion: Roller bearings are suitable for applications that have rotational motion since they can accommodate radial as well as axial loads. This makes them ideal for automotive components, industrial equipment and machinery which are required to work in a smooth and controlled/precise manner.
- High-Speed Applications: Industries in the field of automotive, aerospace, and industrial machine tools use roller bearings extensively because they offer reliable and effective solutions when working with severe speed parameters. This allows the bearings to withstand the increased centrifugal forces and maintain stability even in high revolutions.
Satisfying these common application criteria, roller bearings obtained the right strength, reliability, and efficiency for a multitude of industrial sectors, making them a favorable option in a good number of equipment and machinery applications.
Industries that use roller bearings
let us now examine the sectors that make extensive use of roller bearings. These are stress-bearing and motion components, and hence, there are a number of areas that use them. Among some of the major industrial users of roller bearings are:
- Automotive: In the automotive engineering section, roller bearings are of utmost importance in applications such as wheel assemblies, transmission systems and engines as they provide smooth and operational rotations whilst reducing the friction which optimizes the vehicle as a whole.
- Aerospace: The aerospace industry can make use of roller bearings for such conglomerates as aircraft engines, landing gears, and airframe parts. They are capable of enduring extreme working conditions, enabling them to demonstrate accurate movements in high stress situations.
- Industrial Machinery: Beginning from heavy machines to small toleranced instruments, roller bearings are found to be an imperative aspect in many industrial applications. They are found in systems such as pumps, conveyors, machine tools and many more systems that require strong and smooth motion.
- Construction and Mining: During construction and mining, rollers have bonded to be important as they damp shock and vibration and carry massive weights in machinery such as excavators, loaders, cranes, and drilling rigs, which any enclosed or coaxial would tell their lifespan and usability.
- Railways: Construction of various components such as assemblies, traction motors and axel boxes purely relies on roller bearings in the railway industry with other applications as well, together with the wheels roller bearings assist in displacement thus bringing comfort to the passengers with less risk of failure.
- Energy: The energy sector utilizes roller bearings for several pieces of equipment that include turbines and generators, and even wind turbines. They can operate at high speeds, carry heavy loads, and deal with extreme temperature changes, thus enhancing dependability and efficiency.
It is clear there are countless applications of equipment and machinery where roller bearings are directly installed due to the wide variety of industries that make use of the roller bearings. In addition, these components help in efficiently performing the tasks which the equipment operates. Indeed, these components form an integral part of the machinery assemblages.
Benefits of using roller bearings
let us discuss the advantages roller bearings have. Such elements are quite useful and, therefore, widely employed in different applications. The benefits include but are not limited to the following:
- Handling Radial and Axial Loads: Due to their ability to take both radial and axial loads, roller bearings are fitted on equipment which works against forces which act in all directions from within. This feature helps in improving the functionality and reliability.
- Suitability for High-Speed Applications: Since roller bearings are engineered to fan out rotational speed, they can be effectively implemented in various sphere where fast motion is required. Their effective construction helps to reduce the friction and heat generate,d thus allowing smoother operation at elevated speeds.
- Comparison with Spherical Bearings: Roller bearings provide stunning mileage with respect to spherical bearings. These include increased load carrying capability while maintaining the size, superior precision and a greater resistance to wear. Moreover, the bearings also provide much greater tolerance in terms of misalignment which enhances the overall performance.
In comparison to ball bearings, roller bearings offer several unique benefits:
- Performance at High Speeds: When it comes to high operational speeds, roller bearings are of great benefit as measures are in place to ensure performance requirements are met as their structure allows for a bearing to deploy effective load distribution, cyclopean resourc.
- Load Capacity Differences: Load differences also come about in terms of capacity, and what is noticeable is that roller-bearing housings exhibit an increased load capacity compared to ball-bearing. Due to the presence of rolling elements in roller bearings, wider areas are used to absorb hefty loads so as to withstand higher force,s which are synonymous with roller bearings.
- Choosing the Right Type of Bearing: Each application has different requirements which means that it is important to determine bearing type and dimensions so as to eliminate the need for cut-off races. In specific applications, the load, working speed, volume, and location can determine whether a roller bearing would suffice or a ball bearing instead.
It is important to know the performances of roller bearings as well as those of various bearings so as to make effective choices when replacing a required bearing.
What are the advantages of tapered roller bearings?

As it is known, tapered roller bearings have many benefits. Some of the notable benefits are as follows:
- Handling Radial and Axial Loads: Considering their tapered shape, these bearings are able to accommodate both radial and axial loads, which makes them quite flexible and adaptable for many uses. This helps them to increase their capacity by spreading load across more parts thereby enabling them to lift more loads and withstand more forces in the process.
- Suitability for High-Speed Applications: Tapered roller bearings are ideal for high speed applications. This is because Tapered roller bearings have unique designs that can be manufactured to high tolerances coupled with their ability to withstand high centrifugal forces due to their unique cellular structure. This enables industries where rapid rotational movement is essential which makes them seek out such bearings.
- Comparison with Spherical Bearings: Tapered roller bearings are superior in a number of aspects to spherical bearings. They perform better at high speeds and tolerance for higher load capacity, and the application area requires movement with great angles of wrist rotation and relatively lower axial rotation. Tapered rollers also have a longer lifespan and require less maintenance.
In light of these merits, you can opt for tapered roller bearings with the assurance that they will adequately address your needs and expectations in performance and reliability in the respective application.
Handling radial and axial loads
let’s explore the handling of radial and axial loads in tapered roller bearings. Tapered roller bearings excel in managing both radial and axial loads, making them versatile and suitable for various applications. By design, these bearings can accommodate both types of loads simultaneously, ensuring smooth and efficient performance even in demanding conditions. This unique capability allows tapered roller bearings to effectively handle forces that act in different directions and maintain stability, making them a reliable choice for industries that require precise and reliable movement under heavy load conditions. Whether it’s supporting radial loads, axial loads, or a combination of both, tapered roller bearings provide the necessary robustness to handle diverse load requirements.
Suitability for high-speed applications
Due to your experience in the related field/s, while one considers tapered roller bearings, let’s now examine how radial and axial loads are accommodated – where tapered roller bearings seem to provide an advantage in design as they are able to deal with radial and axial loads simultaneously It is impossible to imagine or design such bearings, as it is done in such a way, that they are very even able to work under tremendously difficult conditions. The line contact structure leads to the rollers having to withstand considerable transverse load. This factor makes tapered roller bearings capable of supporting multiple axial loads and also fitting in applications where axial movements give a lot of trouble. This is a load-supporting type that incorporates radial loads and also axial loads, and both of these are quite normal in many scenarios involving load transfer.
Comparison with Spherical Bearings
In the case of applications with increased speeds, tapered roller bearings have an edge over spherical bearings. Although spherical bearings are able to fit a joint that does not line up properly and enables smooth rotation in many applications, because of their design features they may not be favored in the case of high- speed operations.
- Performance at High Speeds: Because of the design of elements of their construction, mainly the taper of the rollers and raceways, tapered roller bearings are, in general, intended for high-speed applications. This particular shape facilitates optimal force distribution and minimizes the development of friction, which assists in the attainment of smooth rotation even at high speeds. In contrast, spherical bearings could create a larger amount of friction and heat generation, which could limit performance at high speeds.
- Load Capacity Differences: Besides the radial load, tapered roller bearings are also capable of carrying axial load and therefore are suitable for use in applications where radial and axial loads are acting in different directions. On the other hand, spherical bearings have been widely used in facilities that have a misalignment between the shaft and housing, although their load capacity is small relative to tapered roller bearings.
When selecting the right bearing for your specific application, it is critical to contemplate the requirements of your high-speed operation, the magnitude and orientation of the involved loads, and the level of performance and reliability expected.
Taking into account the need to distinguish between roller and ball bearings and their characteristics with respect to the requirements set out in your application, this will allow you to use such bearings with maximum efficiency.
How do roller bearings and ball bearings compare?

there is the aspect of ‘high speed bearing performance’, ‘load carrying capacity differences’ and ‘bearing selection’ that comes into consideration when comparing roller bearings and ball bearings.
Performance at high speeds:
Due to the load that the roller bearing manages to cover across the outer surface while at the same time creating a lower-level cylindrical profile, these bearings operate best in high-speed environments. Consequently, there is a decrease in friction or the generation of heat, allowing for a higher speed of operation. On the other hand, ball bearings can have higher speeds, although they are better suited for applications that do not exert much radial or axial load.
Load capacity differences:
The utility of cylindrical roller bearings is most pronounced, where considerable radial and axial loads exist simultaneously in various planes. Such bearings are more efficient than ball bearings since their structural design allows them to bear more loads and withstand great stress, giving them better durability. However, it should be emphasized that the load capacities of spherical bearings are probably less than those of tapered roller bearings.
Choosing the right type of bearing for your needs:
It may be necessary to make a differentiation between inner and outer race contact, so one should take into account the specific application for which the roller bearings or ball bearings are being selected. Certainly, operational speed, bearing loads in terms of direction, their magnitude, and the performance and reliability targets set for the bearing should be considered too and understood as well during proper differentiation of these bearing types. This understanding, along with the analysis of the specific characteristics of the bearings in terms of the functional requirements of the application, helps to provide recommendations on making an appropriate selection.
Performance at high speeds
it is advisable to note that the performance of roller bearings and ball bearings at high speeds is related to their design features. Generally, for high-speed requirements, roller bearings are recommended since they have wider contact areas. The rolling elements of roller bearings carry the load on a wider area, thus reducing friction and heat generation. This enables roller bearings to work with higher rotational speeds without compromising on efficiency and durability. On the contrary, ball bearings have a smaller contact area, which makes it hard to work at higher ball speeds because of increased friction and heat. Therefore, in applications where high speed is the norm, roller bearings that are designed for such conditions should be selected.
Load capacity differences
there is a need to appreciate some of the differences that exist between the load capacities of roller bearings and ball bearings. A bearing’s load capacity is the weight or force it is designed to bear. In most instances when a comparison of roller and ball bearings is made, it is observed that roller bearings have greater load capacity because they have a wider area of contact and hence can spread the load over a wider area, thus making them suitable in applications where there are big loads and high forces. However, in most cases, ball bearings load capacity is less since the area of contact is smaller. These are more applicable in cases where light loads and smooth and accurate motion are required. Therefore, ensuring that you select the right type of bearing based on the requirements of your application is essential, as choosing a bearing that underperforms may result in downtime in the bearing.
Choosing the right type of bearing for your needs
I have a strong belief that the choice of a bearing is very much application-specific, and here are some key factors to consider when it comes to purchasing bearings for your needs: As an industry expert, it is quite ideal for gluing:
- Load Capacity: As a first step, ascertain the load or force that the bearing is expected to support. Due to their large contact area and their ability to bear a more significant load, roller bearings are usually more appropriate for high loads or forces. Ball bearings on the other hand tend to concentrate under the lighter load and where the application of motion is considerably smooth and controlled.
- Speed and Precision: Take into account the speed of operations of the bearing and the degree of accuracy necessary. In addition to this, ball bearing frequently possesses higher speed ratings, and has a wide range of applications such as those which require high speed of rotation or even high precision. Conversely, roller bearings may be favorable for low speeds or applications where accuracy is not critical.
- Environmental Factors: Evaluate environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and contamination. There are some bearings which have better resistance against harsh environmental conditions than the others. It is very important to choose the correct type of bearing based on the required environmental conditions of use in order to achieve the best results and the longest life expectancy.
- Maintenance and Lubrication: Also, consider the need for maintenance and lubrication. Some form of bearings may demand frequent maintenance and the application of lubricants in order to extend their lifespan and guarantee functionality, while others may be self-lubricating or require no maintenance at all.
Taking into account these elements, and speaking to a bearing specialist, you are better informed and are consequently able to decide and select the right type of bearing that will suit your requirements in turn guaranteeing dependable and effective performance in your application.
Reference
- Roller Bearing Types: Engineering Reliability and Efficiency – This source provides a comprehensive guide to different types of roller bearings.
- Choosing the Right Roller Bearings: A Comprehensive Guide – This guide helps in selecting high-quality roller bearings for industrial applications.
- Rolling Bearing: Types and Applications – ISK BEARINGS – Offers detailed information on various types of rolling bearings and their applications.
- Understanding the Various Types of Roller Bearings – Discusses different types of roller bearings and their functionalities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the common types of roller bearings available?
A: Common types of roller bearings include cylindrical, needle, tapered, and spherical roller bearings. Each of these types is designed to meet specific application requirements, providing various levels of load capacity and performance.
Q: How do roller bearings compare to ball bearings?
A: Roller bearings are used to support heavier loads and are generally more durable than ball bearings. While ball bearings are ideal for applications requiring high-speed rotation with lower loads, roller bearings can carry heavier loads over longer periods with less wear.
Q: What are the applications of roller bearings?
A: Roller bearings are used in a variety of applications, including automotive, industrial machinery, and aerospace sectors. They are ideal for heavy-duty tasks and can support both radial and axial loads, making them versatile for different mechanical requirements.
Q: Why are cylindrical roller thrust bearings important?
A: Cylindrical roller thrust bearings are crucial because they can accommodate heavy axial loads and provide high stiffness, making them suitable for applications where axial load handling is critical, such as in gearboxes and heavy machinery.
Q: What are needle roller bearings, and when are they ideal?
A: Needle roller bearings are a type of rolling-element bearing characterized by their thin and long rollers. They are ideal for applications where space is limited, and high load-carrying capacity is needed, such as in automotive transmissions and portable power tools.
Q: How do roller bearings meet specific application requirements?
A: Roller bearings come in various designs and materials to meet specific application requirements. Factors such as load capacity, speed, temperature, and environmental conditions are considered when selecting the appropriate bearing type for optimal performance.
Q: What are the benefits of using cylindrical bearings?
A: Cylindrical bearings are ideal for applications that require high radial load capacity and low friction. They are commonly used in electric motors, pumps, and gearboxes, where efficiency and reliability are paramount.
Q: How do types of roller bearings support industrial applications?
A: Industrial applications often demand robust and efficient components, and the types of roller bearings available are designed to support these needs. By offering high load capacities and durability, they ensure smooth and reliable operation of heavy machinery and equipment.
Q: What are the differences in load capacity between ball and roller bearings?
A: Ball bearings are typically used for lighter loads and higher speeds, whereas roller bearings can carry much heavier loads due to their larger contact area. This makes roller bearings suitable for more demanding applications.
