The smooth functionality of your wheels heavily relies on wheel bearings. They are small elements that have the great purpose of decreasing friction while accommodating the weight of the vehicle during the rotation of the wheels. Wheel bearings, like other car parts, are prone to damage, but their efficient function is crucial for the automobile. In this blog, I aim to go over the typical root reasons for the deterioration of wheel bearings and help you get a general grasp on their mechanical components, how external factors can affect them, and what the indicators of an issue are. This translates to helping the drivers take proper actions to maintain the reliability of their cars and extend the use of their wheel bearings.
What are the most common causes of wheel bearing failure?

Rotary bearing failure is due to a variety of causes, such as contamination, overheating, melting, lubrication, and other factors that are closely related to wear and tear. Most contaminants, usually dirt, water, and debris, can easily penetrate and cause damage and cut down the efficiency of the project. Heat dissipation can also be caused by friction, which can happen if the object is not lubricated or leads to a huge drop in the object’s lifespan. Apart from all the above-mentioned drivers, such as potholes, unbalanced wheels, and overloading can put a strain on the metal sheath, which results in premature and thermal wear for the bearings. To reduce such issues, routine inspections and maintenance lead to a reliable solution.
How does poor lubrication affect wheel bearings?
Lack of lubrication affects wheel bearings by inducing friction which results in excessive heat production and rapid wear of the bearing parts. Consequently, bearing components are rendered useless because of surface damage and subsequently lower performance. Proper lubrication ensures that the amount of friction is kept low; thus, overheating is avoided and the life of the bearings is increased.
Can hitting potholes damage wheel bearings?
Indeed, hitting potholes can affect wheel bearings. Sudden impacts and shocks in the way of a pothole can be too much for the wheel assembly to handle. From what I have learned, misalignment, cracks, or deformation can all happen to bearing components – this means that they have suffered some type of damage. In any case, it is better to steer clear of any rough road conditions because all of them, even the less serious ones, when taken in repetition, can lead to early bearing breakdowns. Consistent checking might save you from permanent damage.
Does water contamination cause wheel bearings to fail?
Indeed, contamination of water can result in the failure of wheel bearings, and there’s a specific reason for it, which I’ll explain below. Water bears into the bearing assembly, which distorts the environment so that wheel bearings function properly. Here’s a list of the main parameters that are disturbed:
- Lubrication Breakdown – Keeping the intercepting structure lubricated is essential to minimize friction and wear. Bearing lubrication deteriorates or becomes diluted by water combined with the grease and oil components inside the bearing. This protects the appropriate translation layers poorly, resulting in rapid degradation of the component.
- Corrosion – The bearing assembly is adversely affected by the water, along with rust and corrosion of the internal metal surfaces. Under lower amounts of moisture, pitted surfaces are formed, which lowers the effectiveness of the bearing over time. Corrosion affects the parts of the assembly and lowers its structural integrity.
- Contaminant Entrapment – Bearing water usually contains dirt and other solids that may badly wear out the components of the bearing system as they infiltrate the bearing system. Other types of debris embedded in the grease can behave as contaminants, which also damages and wears the assembly out.
- Temperature Changes –Temperature fluctuations and water intrusion into the parts may cause condensation within a set which is then sealed. It makes the system moist, leading to the internal lubrication deteriorating faster and the parts rusting over time.
Protecting wheel bearings from water is one thing I like to recommend the most. With the use of quality seals and regular inspection, moisture should not be able to enter the bearing assembly. Furthermore, one should also ensure proper maintenance procedures are followed such as washing and reapplying grease when needed, as this significantly enhances the operating hours of your wheel bearings.
How can you tell if a wheel bearing is going bad?

My usual diagnosis of a faulty wheel bearing starts with looking for a few signs that most of the experts in the field agree are reliable. One of the signs I also consider the most common is the noise that is not usual for the vehicle, like humming, growling, or, the most severe of all, grinding, especially when the car is in motion. As the stress on the bearing increases, noise seems to worsen when making turns. I also consider shaking or wobbly steering wheels to be an indicator as well, as these physical signs mean excessive play in the bearing. What’s more, bulging or inconsistent tire traction may also be a sign as well because this will change the way that the wheels move, providing less stability. Lastly, I look for all the signs of a failed wheel bearing, if there is concerning heat near the axle or if it has started having any sort of fractures.
What are the typical sounds of a failing wheel bearing?
Most people I have dealt with usually describe the awful noise caused by a failing wheel bearing as a huge howling sound. However, this is not the only noise that can be produced by A wheel bearing. The following analysis aims to list the other sounds and possible reasons for their occurrence:
- A growling or humming noise – Among the sounds produced by the car, this is the most common, and considering the speed of the vehicle, it has a bass tone or rumble sound with a shifting octave. It occurs due to irregular revolutions for the reason that bearing surfaces are either damaged or worn out.
- A clicking or snapping sound – Clicking accompanied by sharp turns can be a sign of either inadequate lubrication, where the internal components of the wheel bearing begin to wear out, or a complete malfunction of the component itself.
- A grinding noise – Griding is perhaps the more severe one in the automobile noise warnings because the bearing showing signs of grinding has Internal damage, which means metal parts are making contact, and this requires urgent servicing.
- A howling or whining sound – The noise will be heard when the speed is increased and rotation of the bearing is unable to lubricate, thus causing wear and tear leading to parts friction.
- Uneven noise patterns – Other times, the load or the direction in which the vehicle is being driven will slightly change the noise level, and these are instances that help determine whether the bearing in question belongs to the left or the right side.
How movements impact these sounds is something that has to be stressed, too. A great tip for diagnosis is to be attentive to details; for example, if the noise seems to get quieter or louder on turns, that might help you identify which side or which wheel applies. If you see these symptoms, tendencies, or features, it is necessary to rectify the situation as soon as possible in order not to exacerbate the driving conditions.
How does a bad wheel bearing affect vehicle handling?
A bad wheel bearing seems to be the one issue that, despite its insignificance, tends to grow faster than any other problem. In my experience with cars, poor wheel bearings usually start off small and escalate quickly. So when the wheel bearing starts failing, the stability of the wheel is put at risk, which means a wash in steering accuracy and general control. You may have trouble maintaining a straight line at high speeds, or you may notice the car pulling towards one side. Furthermore, poor wheel bearings introduce additional friction, which directly leads to vibration and instability, which means a loss of comfort and makes the car feel very sketchy to drive. The issues posed by a degraded wheel bearing also warrant timeliness in replacement to ensure the proper functioning of the car and, most importantly, safety.
Can driving through deep water damage wheel bearings?

It is indeed true that wheel bearings can be damaged when not submerged deep underwater. Water can permeate the bearing housing, pushing out grease or lubricant, further leading to rusting. Over time, this affects friction, leads to wear and tear, and ultimately, the wheel bearing gets damaged. So the best thing is to stay away from deep water, and in case you do get exposed to it, check the bearings afterwards.
How does water enter the wheel hub assembly?
Moisture intrusion into the wheel hub assembly can occur due to faulty seals or gaps in the structure. Based on my experience, even slight degradation or damage of the seals can permit water ingress, such as when fording through deep water or in moderate to heavy rain conditions. If the water gets inside, it emulsifies with the grease, thereby obviating its functional capability, causing rusting corrosion and contamination in the long run. Dust or deformities of the seals means that they should be checked as is standard practice to prevent water intrusions, hence regular inspections are important.
What happens when water contaminates wheel bearings?
Water intrusion in wheel bearings is a serious issue because it affects their lubrication and leads to an increased rate of wear. Wheel Bearings are expected to function under high loads, therefore, grease which is the lubricant in the bearings is required to function as it’s meant to reduce friction. If the grease loses its form structure, then the members will be subjected to higher temperature and friction and will get eroded sooner than expected. Once this situation is aggravated by the water intrusion, it creates conditions for rust and corrosion and ultimately wearing off the bearing surfaces and decreasing their durability. If these issues are not addressed, it leads to complete loss of the bearing,which is a potential safety threat and an expensive repair. To eliminate these threats, regular checkups and timely maintenance is essential.
Do heavy loads contribute to premature wheel bearing failure?

Yup, excessive loads can play a huge role in the early-stage decommissioning of a set of wheel bearings. Personally, I’ve seen that the load ranges of the bearings are built for specific use case scenarios, but over-usage in those limits puts a lot of stress on the parts. More weight means more pressure, increasing heat, which in turn wears out the lubricants themselves. Sooner or later, this might culminate into distortion or thermal stress of the bearing components, and ultimately break it apart. So, appropriate handling of the load and not allowing the trucks to be loaded heavily is one of the measures taken to increase the overall life of the wheel bearings.
How do excessive loads affect wheel bearings?
High amounts of load will place more heat and stress on equipped wheel bearings. This causes rapid material deterioration, failure of lubricant, and, in some cases, even material deformation. After a period of time, applying this load/ this level of strain on the bearings would cause the bearing to deform, cause bearing fatigue, and really cause failure. So, in this case, it is essential to comply with the recommended loads.
Can towing cause wheel bearings to go bad faster?
Based on what I’ve observed, towing can indeed lead to faster wear of wheel bearings. When a vehicle is used for towing purposes, the additional weight puts a strain on the wheel bearings often beyond the limits set for the load capacity. This excessive stress can result in the production of more heat and friction than the oil or grease can withstand, causing these parts to wear out too soon. To make things easier, always check the inscribed towing capacity of the vehicle and check active wear on wheel bearings or damage, then make appropriate inspections.
Are there any preventive measures to extend wheel bearing life?

Such measures include the notion of routine maintenance of wheel bearings as well as taking care of a vehicle’s overall load-bearing capacity, the latter being crucial when towing. Also, entirely prevent driving through deep water and mud as these elements lead to early contamination of bearings. Together, they will ensure the optimal performance of a vehicle. Such maintenance may also promote further use of such elements and a good practice is to eliminate any kinds of vibrations and unusually loud noises.
How often should wheel bearings be checked?
In my opinion, I would check the wheel bearings at least once every 25,000 to 30,000 miles or during the regular brake check. But this may not be the case with some vehicles due to a number of factors, so be sure to consider these parameters:
- Driving Conditions: Those who regularly drive on bumpy or uneven roads or in extreme weather conditions may need to schedule the inspection of their wheel bearings more frequently since this can accelerate wear.
- Vehicle Usage: If the vehicle is heavy-duty or used for towing, it puts more strain on the wheel bearings, hence increasing the need for an inspection for the safety and performance of the vehicle.
- Manufacturer Recommendations: Always take into consideration the maintenance schedule supplied by the manufacturer of the car regardless of whether it seems reasonable to you. Models may specify certain intervals at which the wheel bearings need to be checked.
- Signs of Wear: Even when the mileage interval recommended by the manufacturer is fairly far off, keep cautioning yourself about the early warning signals such as a grinding sound, strange vibration, or tire wear, which are abnormal. A bearing issue might be the cause, and it would necessitate immediate care.
On a regular basis, you should be able to observe if there are any problems with the configuration and ensure that your wheel bearings are maintained properly. If you take these measures into account and are proactive in how you go about your Cup Care, you ARE NOT going to have any issues, so to speak.
What role does proper wheel alignment play in bearing longevity?
Correct wheel alignment is vital in prolonging the life of the wheel bearings, but in my experience in the industry, it is one of the most neglected factors. Bearing loads are uniformly distributed, and smooth operating conditions are obtained when other parameters, such as wheel alignment, are taken care of. On the contrary, misalignment results in unevenly applied pressure and enhances the rate of bearing wear, overheating, and, ultimately, the failure of the bearing. I always tell my clients that if they check the alignments regularly, especially after they collide with curbs or potholes, they will not have to deal with expensive fixes in the future. This is a small procedure that provides optimum performance and enhances the life of all your bearings, devices, and multiangular.
When should you replace a wheel bearing?
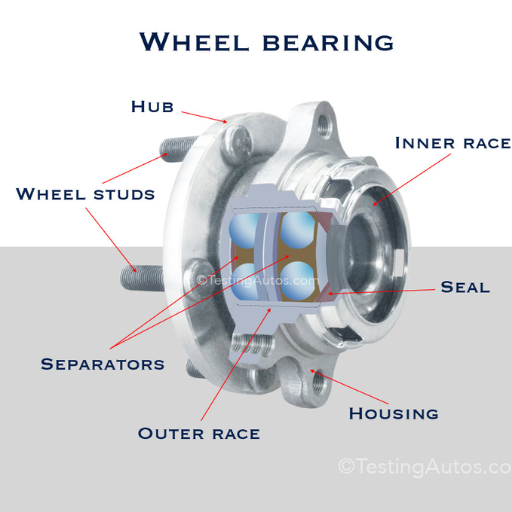
It is ideal to change the wheel bearings once you realize the signs of wear and tear or signs of fault. Some of the telltale signs include noise in the form of grinding or growling from the wheels, vibration of the steering wheel, or one side of the tire wearing out more than the other. In such cases, timeliness is very important as delaying will only cause more strain and risk of being unsafe. Moreover, replacing the wheel bearings on time also makes the vehicles run better.
Is it necessary to replace both wheel bearings at once?
No, wheel bearing replacement is not a must for pairs. In most instances, clients are told to replace both bearings; however, in the case one shows damage, then I – advise replacing only the faulty one. One change does not bring failure on the opposite wheel assembly, which, in fact, some bearings do in their lifetime oiling and driving conditions. Again, yes, but I do tell them to check the other bearing as well during the replacement just to rule out that there are no problems with it.
How long do quality wheel bearings typically last?
It’s not uncommon for good-quality wheel bearings to last anywhere from 85,000 to 100,000 miles when driven under normal conditions. However, they can be influenced by a little constructive such as the quality of the road, weather conditions, and driving patterns. Good care and keeping an eye out for the signs can help enhance their lifespan.
Reference
- 5 Reasons for Wheel Bearing Failure – This article discusses common reasons for wheel bearing failure, such as driving through deep water and poor road conditions.
- What would cause repeated wheel bearing failure? – A forum discussion that explores causes of repeated wheel bearing failure and potential solutions.
- Wheel Bearing: How Do I Know if I Need a Replacement? – This guide from Kelley Blue Book explains how to identify when wheel bearings need replacement and factors that contribute to their wear.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the common causes of wheel bearing failure?
A: Wheel bearings can fail due to several reasons, including contamination from water or dirt, lack of lubrication, excessive heat, and normal wear and tear. Poor quality wheel bearings, improper installation, and higher loads on the wheel can also contribute to premature failure. Additionally, impacts from potholes or curbs can cause stress on the bearings, leading to damage over time.
Q: How can I tell if a wheel bearing is bad?
A: Signs of a bad wheel bearing include unusual noises like grinding, humming, or rumbling, especially when turning. You may also experience vibrations in the steering wheel or through the vehicle’s floor. Uneven tire wear, loose steering, or the vehicle pulling to one side can also indicate a failing wheel bearing. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to have a mechanic check your wheel bearings.
Q: How often should wheel bearings be checked or replaced?
A: Wheel bearings typically don’t have a specific replacement interval, as their lifespan can vary greatly depending on driving conditions and vehicle type. However, it’s a good idea to have your wheel bearings checked during routine maintenance, such as tire rotations or brake services. Many wheel bearings last 100,000 miles or more, but if you notice any signs of failure, you should have them inspected immediately.
Q: Can driving with a bad wheel bearing damage other parts of my vehicle?
A: Yes, driving with a bad wheel bearing can cause damage to other components. As the bearing deteriorates, it can affect the hub, CV joint, and even the transmission. A severely worn bearing might allow the wheel to wobble, potentially damaging the tire, rotor, and brake caliper. In extreme cases, a completely failed bearing could cause the wheel to seize or separate from the vehicle, leading to a dangerous situation.
Q: Are front wheel bearings more prone to failure than rear ones?
A: Front wheel bearings often experience more stress and wear than rear ones, especially in front-wheel-drive vehicles. This is because front wheels bear more weight, handle steering forces, and transmit power in front-wheel-drive cars. However, rear wheel bearings can also fail, particularly in rear-wheel-drive or all-wheel-drive vehicles. The failure rate can vary depending on the vehicle design, driving conditions, and maintenance.
Q: How can I prevent premature wheel bearing failure?
A: To prevent wheel bearing failure, ensure proper maintenance of your vehicle. This includes avoiding deep water or mud that could contaminate the bearings, being cautious of potholes and curbs, and maintaining proper tire pressure to reduce stress on the bearings. Regular inspections by a qualified mechanic can catch early signs of wear. When replacing bearings, use high-quality parts and ensure they are installed correctly to prevent premature wear and failure.
Q: Is it necessary to replace both wheel bearings on an axle if only one is bad?
A: While it’s not always necessary to replace both wheel bearings on an axle if only one is bad, many mechanics recommend doing so, especially if the vehicle has high mileage. This is because if one bearing has failed, the other is likely to be wearing out as well. Replacing both can save time and money in the long run, as you’ll avoid a second repair in the near future. However, the final decision should be based on the mechanic’s assessment and your budget.
Q: How long does it take to replace a wheel bearing?
A: The time it takes to replace a wheel bearing can vary depending on the vehicle make and model, as well as the type of bearing. On average, it can take a skilled mechanic 1-2 hours to replace a wheel bearing hub assembly. However, some vehicles may require more time if the bearing is pressed into the hub or if other components need to be removed to access the bearing. Always consult with your mechanic for a more accurate time estimate for your specific vehicle.
