This post serves as your one-stop shop guide for everything ball bearing related, their functions, categories, good and bad parts, and even how they withstand radial and axial loads. Want to know how ball bearings function in daily gadgets, or how many types of ball bearings there are and their advantages? This article will be all that you require. Join us on this riveting journey as we explore the different facets of ball bearings and their importance in the engineering and automotive industries!
How are ball bearings used in everyday applications?

it is evident that ball bearings have a diverse scope of application in ordinary tasks. The movement of machines and other tools has been simplified through the reduction in friction, which they assist in. Some of the examples listed below show the key role ball bearings play in modern day-to-day functioning:
- Automotive Industry: Ball bearings form integral parts of automobiles; they are used to facilitate the movement of the engines, undergo smooth transmissions, allow the wheels to rotate, and assist the steering systems of the vehicles.
- Industrial Machinery: Ball bearings such as pumps and conveyor belts are now integrated into industrial machinery in order to improve their efficiency and longevity and reduce the amount of energy consumed during usage.
- Household Appliances: Washing machines, power tools, refrigerators, and fans are examples of common household appliances that utilize ball bearings to enable better functionality by allowing parts within the machine to rotate smoothly.
- Electric Motors: Appliances, automobiles, and industrial equipment utilize electric motors, which have a shaft that spins; within the motors are ball bearings that ensure there is minimal friction during rotation, allowing the performance of the device to be excellent.
- Computer Hardware: Hard disk drives and cooling fans in computers utilize ball bearings as they assist in movement while minimizing the amount of noise and vibrations generated.
These are just a few illustrations of the various ways ball bearings are found in practical use. Their high usage in many sectors is a demonstration of their usefulness in providing smooth and dependable operation of a number of mechanical systems.
What is a ball bearing, and how does it function?
A ball bearing is known to be a type of rolling element bearing which has a basic function to control the friction and motion between two or more interacting surfaces. Such a device includes an inner and outer ring with small balls made of some metal inserted between them. These act as the rolling elements and hence assist in bearing the pressure while friction is reduced as the surfaces rotate against each other.
A ball bearing operates on a rolling contact principle. The moment a load is transferred onto the bearing, the balls allow the inner and outer rings to rotate while registering close to zero friction. Such capability enables and facilitates motion in a smooth and efficient manner, thereby considerably limiting energy losses and providing flawless performance in a multitude of mechanical components.
Employing ball bearings in a machine or some equipment provides great control of motion, noise, and vibration suppression, as well as increased efficiency. Their design and construction allow them to work at high speeds and exert both radial and axial forces, so they are a requirement in various industrial applications.
In this article, we will examine the various industries where ball bearings are in the market and further examine the merits that they add to the machine.
Common industries where ball bearings are used
let us delve into the emerging industries that employ ball bearings and appreciate the importance of these components in machine engineering. Owing to their multifaceted form and distinct features, ball bearings are employed across industries. Below are some of the major industries in which ball bearings are important:
- Automotive Industry: The automotive industry makes use of ball bearings in a plethora of applications, such as for engines, transmissions, wheel hubs, steering, and electric motors. It makes sure that ideal functionality is reached by ensuring the friction is significantly decreased and reliable motion management is provided.
- Manufacturing and Industrial Equipment: From Construction equipment and Conveyors to Robotics and Machine tools along with an impressive array of industrial equipment, ball bearings are integral in being used as motion control devices. This bolsters energy efficacy while further ensuring that equipment performance is optimum.
- Aerospace and Defense: In the world of aerospace and defense, ball bearings command heavy respect due to their usage in Aircraft engines, missile systems, and Radar equipment. They allow for precise movement when working with high loads, pressures, and extreme temperatures.
- Medical Equipment: Surgical equipment, imaging machinery dental equipment as well as patient care systems all have one thing in common, the need for bearings. Ball bearings allow for a smooth, precise, and reliable system while limiting friction and guaranteeing the lifetime of the device.
- Electronics and Appliances: Printers, Electric motors, Refrigerators, Washing machines, and HVAC systems are examples of devices that utilize ball-bearing elements for generating rotation. Implementing ball bearings translates to the reduction of noise being produced while increasing the overall performance of the equipment.
Integrating ball bearings into these sectors helps manufacturers attain greater accuracy, extend the lifespan of the equipment, minimize idle time, and increase productivity. Their diverse design and construction enable them to be critical to sustaining ideal performance in various applications.
Advantages of using ball bearings in machinery
Let’s analyze the benefits that ball bearings offer to machinery with the help of an industry expert.
- Efficiency and Reliability: Ball bearings facilitate seamless and effective revolutions while reducing friction. Performance enhancement is beneficial since it works to reduce energy consumption while boosting productivity at the same time.
- Enhanced Precision: Due to the ball bearings, the engine is capable of an exact and precise movement, which is crucial for the proper functioning of any machine while avoiding errors or inaccuracies.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: The esteemed resilience of ball bearings makes them durable, and hence, there is reduced mechanical wear and tear on the equipment components, making for an offering that lasts longer at lower repair costs while reducing downtime.
- Reduced Noise and Vibration:The use of ball bearings makes it possible to lessen noise and vibration, facilitating a quieter and more comfortable working environment.
- Versatility: Due to the wide variety of shapes, sizes, and configurations, ball bearings can be employed for different purposes in different industries.
- Cost-Effective Solution: In the long run,n ball bearings are cost-efficient because they have an increased lifetime, require less frequent repairs, and have a higher efficiency output.
Integrating ball bearings into the machinery has proven to be an innovative solution that has offered a wide range of benefits, increasing its efficiency and reliability and boosting its productivity.
What are the different types of ball bearings?

In this segment, I will delineate the types of ball bearings available in the industry. Given their suitability for a wide range of applications in various industries, it is understandable that ball bearings come in different configurations. These are the most common types of ball bearings:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings: These overcome the limitations of the thrust elements through the use of deep raceway grooves bearing the ring and the ball, which can then be used in applications that require high radial and axial load capacities. Due to their versatility, they can also be employed in electric motors, household appliances, and the automotive industry.
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings: These types of bearings are built with contact angles that allow for greater thrust load capacity, allowing them to take on both radial and axial loads. They are commonly found in machine tools, pumps, and gearboxes.
- Self-Aligning Ball Bearings: These bearings provide a distinct advantage. They can accommodate shaft deflection and misalignment without the need for additional components. These are often used in conveyor systems, electric motors and agricultural machinery..
- Thrust Ball Bearings: This type of bearing is used mostly for axial loads, but it has the ability to take higher axial loads in one direction. They can be found in automotive transmission, steering systems, and axial fans.
- Miniature Ball Bearings: Because of their small ball bearing size, they cope well with precision instruments, electronics, and medical devices that require limited space and a precise rotating motion.
Different styles of ball bearings do indeed come with advantages relevant to their purpose. Knowledge about the various bearer types aids in the selection of efficient bearings suitable for businesses in various sectors.
Understanding rolling-element bearings
I need knowledge of the Rolling Element Bearin in order to choose a type of bearing that will satisfy the requirements of a particular application. The rolling element is designed for turning motion and some elements are bearing in motion, these components have been fitted to articulate more freely with each other. It comprises two basic parts: an inner race, an outer race, and rolling elements, which may be balls or rollers.
Other variants of bearings are less efficient when compared to rolling–element bearings because of the following reasons:
- Low Friction and Reduced Wear: The rolling components of these types of bearings effectively eliminate contact and friction when sliding, resulting in less energy loss and reduced wear and tear, thus extending the longevity of the machine.
- High Load Capacity: The rolling-element bearings are capable of radial and axial load, which enhances the performance of load-bearing in many applications.
- Precise and Reliable Performance: These bearings are built to high standards of performance and tolerance, which translates into consistent operation even in the harshest conditions.
- Wide Range of Applications: Rolling-element bearings are used in automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and other fields where an object has to rotate and take up a load.
This key insight will inform industry specialists sin electing their required rolling element bearings by explaining their diverse array of performance advantages.
Comparing roller bearings and plain bearings
This is a huge contrast to plain bearings, which, in whichever form they take, utilize sliding friction between the surface of the bearing and the shaft and, thus, produce less friction force but do so at a high cost of bearing loading. I hope Minus possesses a thorough understanding of these core concepts. Moving on, though, I have always been in agreement that roller bearings are much more suitable for high-load applications than fixed bore or plain bearings, which are much more cost-effective and simpler due to their low loading and speed requirements. However, Much like the aforementioned with regards to simplicity and ease, the choice between the two ultimately rests on four primary variables, these being the load-bearing capacity of the device, the speed generated by the device, the precision required for the motion, and bearing as well as the environmental conditions while the only difference is that as we progress through, we add in more. In fisherman’s terminology, the roller bearings are fitted and sealed externally, while the plain bearings come in an encased form, making them easy to use. These are just a few factors that make a significant impact on indoor decisions. Nevertheless, it is paramount to approach these factors with great caution, as such decisions can either ensure the longevity and performance of a device or result in its complete demise.
Special ball bearing types and their applications
I understand different types of unique ball bearings and the special features and benefits they provide for specific uses. Some of them include, but are not limited to:
- Self-aligning Ball Bearings: They have two rows of balls and a concave outer ring, which helps in self-aligning and correcting possible misalignment of the housing and shaft. The bearings can be used in places where it is certain that the shaft will be deflected or will be placed keenly on the conveyor systems, such as some agricultural equipment.
- High-precision Ball Bearings: They are made in such a way that they are very close to their ideal condition with an unprecedented level of accuracy, making them ideal for jobs that require precision or a seamless level of operation. Such use cases would be machine tools, robotics, or medical tools.
- Miniature and Instrument Ball Bearings: These bearings are made to be very small so that they can be used in motors that don’t need much energy, such as those in robots, computer disk drives, or other miniature mechanics. The small size, alongside the low friction, enables a high degree of performance in tight places.
- Thrust Ball Bearings: Thrust ball bearings can bear considerable thrust forces in only one direction because they bear an axial load. It is commonly found in automotive applications, industrial machinery, and agricultural machinery and tools.
- Stainless Steel Ball Bearings: For applications prone to exposure to excess moisture or harsh environments due to the location, such ball bearings need to have rings to prevent corrosion. Industries using food processing and medical devices, including marine equipment, commonly use them.
Naing’s bearings size chart lists all the specialized ball bearing types that have a given tujuan and application in order to offer customized solutions to fit the requirements of different businesses. Knowing about these specialized solutions enables engineers, as well as design professionals, to enhance their decision-making while maximizing the efficiency of the engineering components.
What are the benefits of ball bearings over other bearing types?

I can conclude that ball bearings have certain distinct advantages over the other types of bearings. The following are a few of the advantages of ball bearings which render them the best in a number of applications:
- High Efficiency: The frictional resistance amongst bearing balls is often low, which provides optimal performance, meaning less energy consumption and improved equipment performance.
- Versatility: Most industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, make use of ball bearings but possess radial and axial load capabilities, which allow them to be used for a wider variety of tasks.
- Durability: Ball bearings, with their high-quality material and robust construction, are able to withstand high speeds, heavy loads, and harsh external conditions. This leads to consistent and extended performance.
- Compact Design: They have a small size and lightweight nature, which allows them to fix places that are weight-sensitive or have limited space. Their footprint being small allows the design of machinery and equipment to be done more efficiently.
- Cost-Effective: On top of their efficient design, these bearings hold a competitive price, which only adds to the possibilities they already have. This allows for a decrease in maintenance spending and improves operational effectiveness.
Harnessing these advantages allows engineers and designers to enhance the performance, dependability, and lifespan of their machinery and tools, making ball bearings a preferred choice in numerous industries.
Advantages of angular contact ball bearings
Within wide-ranging mechanical workings, angular contact ball bearings are the most favored choice. With regard to this, let us examine some major benefits of angular ball bearings.
- Improved Load Distribution: Angular contact ball bearings have the feature of withstanding axial and radial loads at the same time. Such constructive disposition gives a chance to carry the loads at bigger contact regions hence increasing the bearing’s overall capability performance.
- High Speed Capability: The construction of Angular contact ball bearings allows for the rotation of the components to high speeds, therefore they can be implemented in systems that require faster rotation. The low friction characteristics of angular contact ball bearings contribute to the reduction of heat, allowing for better performance at greater speeds.
- Precise and Accurate Performance: These bearings are developed for performance that is accurate and consistent. Our preference is determined by the contact angle, which can be altered in order to meet certain performance criteria, in this case, to improve alignment and minimize chances of alignment problems.
- Versatility: The angular contact ball bearings can be found in numerous configurations, sizes, and materials; therefore, they are relevant to many applications. Typical applications include automotive, aerospace, machine tools, NC machines, production tools, robotics, etc.
It is because of these benefits that angular contact ball bearings have become an irreplaceable part in various industries as these allow engineers and designers to enhance the performance, strength, and lifespan of their machinery and equipment.
How do thrust ball bearings handle loads?
Thrust ball bearings function as a single axial load, providing support to high off-centered loads by virtue of their ingenious construction. They have a spherical shape, which allows them to accommodate all angular contact. It is due to this structure that they can be apt for any application that works under low rotational velocities or is required to function under low friction. Thrust ball bearings do exhibit smooth operation and minimal friction but rusting emerges as a drawback. They consist of rolling components that are placed inside a cage. Rolling machinery where excessive wear occurs can rely upon thrust ball bearings. They can endure harsh conditions and offer long-term performance.
Benefits of ceramic ball bearings
ceramic ball bearings have multiple benefits in comparison to steel ball bearings. Some of them are given below:
- Higher Speeds and Lower Friction: Ceramic ball bearings have exceptional hardness and smoothness, resulting in reduced frictional resistance. This allows for higher rotational speeds and improved overall efficiency in various applications.
- Enhanced Durability: Due to their inherent resistance to corrosion, ceramic ball bearings have a longer lifespan compared to steel ball bearings. They can withstand harsh operating conditions, including exposure to chemicals, moisture, and high temperatures.
- Lightweight Design: Ceramic ball bearings are significantly lighter than traditional steel ball bearings, making them ideal for applications where weight reduction is essential. This feature enables faster acceleration, improved maneuverability, and reduced energy consumption.
- High-Temperature Stability: Ceramic ball bearings have excellent thermal properties, enabling them to operate at higher temperature ranges without compromising their performance. This makes them suitable for applications that require heat resistance, such as automotive engines and industrial machinery.
- Electrically Insulating: Ceramic materials are non-conductive, making ceramic ball bearings electrically insulating. This property is crucial in applications where electrical isolation is required to prevent the risk of current leakage or damage due to electrical arcing.
Utilizing the advantages of ceramic ball bearings, industries can accomplish greater performance, toughness, and efficiency of their mechanical systems, ensuring the operation is frictionless and trouble-free even under harsh situations.
How do roller bearings differ from ball bearings?

Ball bearings, as industry constructs, are made to accept radial and axial loads in various applications. Radial loads are normal forces applied about the axis of rotation and axial loads are normal forces applied about the axis of rotation. These loads are something ball bearings are specifically designed to handle.
Ball bearings are made of a casing structure with an outer race and an inner race, both of which have a plurality of balls encased in a cage. A plurality of balls assists in the even distribution of the load on the races, thus minimizing friction and allowing for easy rotation of the antagonistic race. When a radial load is applied to the ball, which is maintaining two races, the ball will at first maintain contact with the outer race until it is forced to rotate, which in turn allows the ball to shift the load onto the inner race, allowing the bearing to now shoulder forces or even weight from numerous axes.
In scenarios dealing with axial loads, including axial forces or thrust, thrust ball or angular contact ball bearings are predominantly employed in mechanical systems. Because of the angle between their balls and their raceways, angular contact ball bearings can bear radial loads and axial loads at the same time. While other ball bearing designs are used to handle thrust component forces, thrust ball bearings are specifically designed to take axial loads wherever they occur in the mechanical assembly.
The use of ball bearings allows equipment and machines to effectively cope with not just radial but also axial forces, enhancing performance and dependability.
Key differences between roller and ball bearings
let’s start with a description of the distinguishing features between roller and ball bearings. Both types are quite important in several applications; however, they have dissimilar design and operational features:
Roller Bearings:
- Design: A cylindrical or tapered roller is a rolling element in a roller bearing that serves the function of spreading the load on a larger surface area
- Load Capacity: Because of the increased contact area, roller bearings are more effective in carrying greater radial loads than that which a ball bearing can carry.
- Friction and Heat: More friction and heat are normally produced by roller bearings as a consequence of cylindrical or tapered rollers rolling.
- Applications: Roller bearings are primarily used in applications characterized by heavy radial loads, such as conveyor drives, automobile wheels, and heavy machines.
Ball Bearings:
- Design: The rolling surfaces of the ball bearings include raceways that contact a single point (ball bearings use balls as their rolling components).
- Load Capacity: The load-carrying rating for ball bearings is lower in comparison to roller bearings; in turn, such bearings work best under operating conditions that require high speed and axial loads.
- Friction and Heat: Because of the rolling action of the balls, less friction and heat are generated in the ball bearings.
- Applications: Ball bearings find broad application in structural parts that need to rotate at a high velocity and need to bear moderate radial loads, such as electric motors, fans, and precision machinery.
Grasping these crucial aspects enables engineers and also designers to choose the most appropriate type of bearing for particular applications, thus enhancing efficiency, dependability, and life expectancy.
Applications best suited for roller bearings.
roller bearings find their optimal application in scenarios where heavy radial loads and shock loads need to be efficiently managed. Their robust design and ability to withstand high loads make them suitable for various demanding environments, such as heavy machinery, construction equipment, and automotive applications. Roller bearings excel in situations requiring durability, longevity, and the ability to handle substantial radial forces. Additionally, their suitability for low-speed operations and the ability to absorb impact loads make them an ideal choice for these demanding applications.
Maintenance and lifespan considerations for roller bearings
the application of roller bearings is justified primarily in the cases of high radial and shock loads. Because of their sturdy construction and load capability, they are used in various high-stress situations, including heavy machines, construction, and automobiles. For applications that require resistance, life span, and large radial load, roller bearings are the best choice. Moreover, they are also the best choice in these difficult conditions because they operate at low speeds and can take impact loads.
- Regular Lubrication: Enough lubrication is critical in order to reduce the friction and wear damage within the bearing. Always adhere to the lubricating instructions given by the manufacturer in regard to type, amount and status of use.
- Proper Installation: Ensure that the correct installation practice is applied in order to avoid any deposition of excessive preload, which might cause misalignment and later bearing damage during normal operation. Follow the manufacturer’s guides and recommended tools for the installation.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider the working environment and take precautions to defend the roller bearings against dust, excessive humidity,y and extreme temperature. Proper seals or shields can protect the bearings from the outside environment practically.
- Monitoring and Inspection: Over the intended lifetime of the roller bearings, perform periodic maintenance in order to check for possible signs of wear, damage, and abnormal noise. Maintenance activity should include regular tightening, inspection for any signs of wear, tests, and other relevant procedures.
- Replacement When Needed: If a roller bearing is grossly worn out, damaged, or failed, the earliest possible replacement is critical in this instance. There is a possibility of causing damage to other parts of the equipment or the entire machinery unit if the faulty bearing is still used.
With regard to the above factors, if you pay close attention to the handling of maintenance procedures, you will extend the life and improve the reliability of the roller bearings, which, in turn, will improve the overall efficiency of your machines/equipment.
How do ball bearings support radial and axial loads?
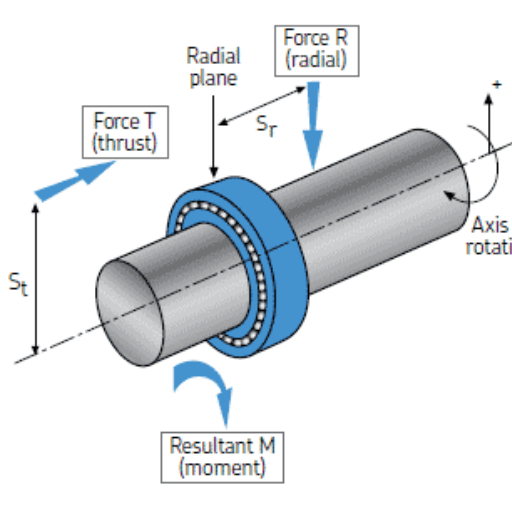
Ball bearings are essential components that, as an industry expert, you would appreciate and execute various applications while supporting axial and radial loads. As part of their fabrication, these components are perfect since they reduce contact between moving parts, lower friction, and thus ensure smooth operation. Here’s a succinct explanation of how ball bearings support radial and axial loads.
- Radial Loads: Ball bearings are engineered to accommodate radial loads, which are loads exerted at right angles on the axis of the bearing. They bind the load between the rolling elements (balls) and the outer raceway, thus facilitating force transfer from a rotating shaft to a static part. This construction allows for all-around contact of the bearing with loads coming from different directions, thereby enhancing rotation stability and smooth motion of the unit.
- Axial Loads: A generic type of sliding bearing is mainly used in ball bearings for supporting radial loads, but some types, such as thrust ball bearings, have been manufactured to take care of the axial loads. Axial loads are forces that are applied along the direction of the bearing axis. A Thrust ball bearing consists of two grooved washers with balls in between them. These types of thrust bearings are designed to handle significant axial loads while enabling the transfer of thrust forces at a desired angle.
Employing ball bearings in machines and devices gives manufacturers confidence in their functioning because ball bearings are capable of efficiently distributing both radial and axial loads, which enables the parts to operate smoothly and with the least possible damage.
The role of deep groove ball bearings in load management
let’s dive into the applications of deep groove ball bearings, primarily their involvement in load management. Deep groove ball bearings are broadly used in numerous applications owing to their high level of adaptability in bearing radial as well as axial loads. In the context of their importance in load management, here is a short response in order to clarify on the same.
Deep groove ball bearings are crucial, in this case, axial load, especially deep groove ball bearings that have the capability of equal distribution of axial and radial loads. They have a deep raceway groove, which allows them to take up excessive radial loads. They are also responsible for the rotatory motion of components and the minimization of friction, ensuring reliable and robust structures of parts and components in different machines. This management of increased loads smoothens the functioning of the system, minimizes the wear and tear of components, and thus improves the overall efficiency of the working system.
In conclusion, deep groove ball bearings are essential when it comes to load management as they help support axial and radial components. Their design and properties that allow them to withstand various different forces help them to be useful in numerous applications.
How self-aligning ball bearings work with misalignment
a self-aligning ball bearing is a type of bearing that is designed for applications where there is some degree of misalignment. These bearings feature two rows of ball elements set between a spherical outer ring raceway and a concave inner ring raceway. Such a distinct structure enables the bearing to function effectively despite having a certain angular displacement between its shaft and housing. In a case of displacement, both rings can rotate around themselves, that is all the inner and outer components do rotate in relation to the other components of the bearing. Because of this, the design tolerances that allow for such displacement are not unduly restrictive because the effectiveness of a real bearing is much less sensitive to such displacements. This is most beneficial during self aligning ball bearing operation, as the smooth functioning of the bearing is ensured even under scenarios wherein a misalignment is to be expected.
Handling thrust loads with thrust bearings
Thrust bearings are the answer to thrust responsibility . These bearings’ specifics are their ability to offer accommodation to axial forces and to develop an application that restrains such forces. In comparison with other bearings, thrust bearings are purposely made for forces that are parallel to the axis of the shaft, making the thrust bearings useful in applications that need to counter heavy axial loads.
Thrust bearings have rolling elements such as balls or cylindrical rollers rotating within a raceway. This arrangement enables the bearing to better cope with axial load applications while reducing wear and tear to the concerned components. The use of thrust bearings allows engineers and designers to enhance the function of the equipment or machinery and increase its life even when large masses of thrust forces are applied.
From automotive transmissions to industrial machines and other high-load types of applications, thrust bearings provide excellent performance with good load-sharing capability and better efficiency. For applications where loads are thrust-focused, the use of thrust bearings in such applications will always be the right choice for the performance required in critical applications.
Reference
- Ball Bearing Types & Applications – EZO USA
- Types of Bearings and Their Applications – JVN Bearings
- What are Ball Bearings Used For? – Lily Bearing
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are ball bearings, and how do they function?
A: Ball bearings are a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races. They function by allowing the bearing races to rotate smoothly while reducing friction between the moving parts of the bearing.
Q: Why are ball bearings ideal for high-speed applications?
A: Ball bearings are ideal for high-speed applications due to their ability to minimize friction, which allows the bearing to handle high rotational speeds efficiently. The design also helps maintain lower operational temperatures.
Q: What are the different types of ball bearings?
A: Types of ball bearings include single-row bearings, angular contact bearings, and hybrid ball bearings. Each type is designed to meet specific requirements in various applications.
Q: How do angular contact bearings differ from other ball bearings?
A: Angular contact bearings differ in that they are designed to handle combined loads, both radial and axial, due to the angle of contact between the bearing balls and the bearing races. This makes them suitable for applications where high precision and load handling are critical.
Q: What applications commonly use ball bearings?
A: Ball bearings are used in a wide range of applications, including automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and consumer electronics, among others. They are chosen for their efficiency in reducing friction and supporting radial and axial loads.
Q: How is the width of the bearing significant in its performance?
A: The width of the bearing is significant as it determines the load capacity and speed capabilities of the bearing. A wider bearing can typically support greater loads and provide better stability.
Q: What are hybrid ball bearings, and where are they used?
A: Hybrid ball bearings consist of steel bearing races and ceramic bearing balls. They are used in applications that require high-speed performance and reduced friction, such as in electric motors and high-speed machinery.
Q: Can ball bearings be used in environments with high temperatures?
A: Yes, certain ball bearings are designed to handle high-temperature environments. These bearings are made from materials that can withstand increased temperatures and are often used in industrial applications.
Q: How do single-row ball bearings function?
A: Single-row ball bearings feature one of the bearing races, and the bearing balls are arranged in a single row. They provide a balance between radial load capacity and speed, making them versatile for various applications.
Q: What is a spherical roller bearing, and how is it different from a ball bearing?
A: A spherical roller bearing is designed to handle heavy radial and axial loads, unlike a ball bearing which is more suited for high-speed applications with moderate loads. Spherical roller bearings are also available for applications requiring misalignment accommodation.
