Wheel bearings are a critical component for smooth and safe vehicle use, allowing wheels to rotate with support and steadiness. However, improper mounting of the nut might result in serious implications such as excessive wear and tear and even complete bearing collapse, which risks the safety and functionality of the bearings. The article provides stepwise instructions on how to tighten the wheel bearing nuts to the desired torque requirements. Hence, this particular article gives you information on wheel bearing nut tightening, which will be useful for all the mechanics and shaft builders out there. In this article, mechanics and builders will be assisted with proper tightening techniques of the wheel bearing nut.
What is a wheel-bearing torque chart, and why is it important?
A wheel bearing torque chart is information necessary for the users in view of the fact it specifies what torque value is suitable for tightening wheel bearing nuts according to any particular manufacturer. In the case of preloading the bearings, this point must be understood since too much or too little torque creates the risk of the bearing working improperly, which then causes a drastic decrease in the wheel’s performance or wears out the bearing too early. The wheel torque has quite a considerable influence on the performance of the vehicle as well as the overall functional capability of the wheel. Such tools also explain the way the vehicle operates safely.
The role of proper torque in wheel bearing longevity
I would like to highlight the fact that the longevity of the wheel bearing is largely dependent on the torque that is applied, and this should also be emphasized further. When it comes to ensuring that the wheel bearings can attain their maximum lifetime, it is really crucial to observe the recommended torque values. This is why:
- Preventing Damage to Bearings: A crushed bearing is a result of nuts that have been overly tightened. If the ring gear bearing is properly meshed within the case, it would also result in increased internal friction, which overheats the whole car, resulting in what you would call failure. Under tight, the right of components gives the assembly a lot of knocks, which results in instability and uneven wear, thus weakening the bearing.
- Ensuring Proper Load Distribution: The aircraft industry works in assembly, which works under a certain load range. Over-tightening or not getting an even torque on assembly leads to uneven or localized stresses, which can be detrimental to the life of any component, for that matter. Manufacturer specifications tend to absorb the load across various components in the bearing by giving a specified torque.
- Avoiding Excess Vibration: Quite a few things will change as a result of overtightening the wheel bearing, such as the assembly having more bolts, which can reduce the dampening effect due to the challenges of the excessive number of bolts. This assembly, once loosened, not only impacts comfort but also decreases the bearing and the components’ lifetime.
- Prolonging Component Lifespan: If one does not use proper torque, not only would bearings be destroyed, but any supporting structures such as seals and so on would also receive damage in the long run. Protecting seals and eliminating extremes of force would mitigate the wear across the assembly.
To use this information correctly, always have the manufacturer’s torque specifications chart with you. It will normally have the value listed in pound-feet (lb-ft) or in Newton meters (Nm). Do not try to do guesswork – there is a wrench for that. Periodic checks and regular preventive maintenance will make sure that your wheel bearings remain in good shape for a long time.
Consequences of incorrect wheel bearing torque
The improper torque of the wheel bearing can result in a number of repairable and non-repairable function-impairing issues with your vehicle. The explanation of these consequences is as follows:
- Premature Bearing Wear or Failure
Excessive bearing wear or failure can occur due to excess or lack of tightening. If the torque is inadequate, the wheel bearing assembly of the wheel, if the proper clutch is not applied, undergoes excessive movement of bearing, which leads to internal damage or even failure over a period of time. On the contrary, excessive tightening would result in the crushing of the bearing component, leading to excess wear or instantaneous failure.
- Excessive Heat Development
Poorly torqued bearing assemblies could lead to an increase in the amount of slavery and low friction. Such friction is in excess and bound to compromise the bearing materials, which leads to overheating, which would further mean that the working life of this assembly would also significantly reduce.
- Reduced Vehicle Performance
Wheels with improper torque can cause insufficient tightening, which could result in misalignment of the other components bonded to the wheel hub. If this occurs, the wheel would end up rotating in a way that is undesirable as it would potentially cause vibrations or result in excessive wear on the tires, which are quite undesirable since they reduce the vehicle’s efficiency and fuel consumption.
- Safety Risks – Brake System Impacts
Worn-out or high-torque wheel bearings can change or move the location of the rotary stone or drum. This poses a great risk to braking performance by increasing the distance and the chances of failure of the braking system during intense situations.
- Damage to Adjacent Components
Due to the failing malfunction of a wheel’s bearing because of improper tightening, the extra scope of stress is applied onto adjacent parts such as axle shafts, wheel hubs, or suspension systems. Eventually, it may result in damages that need expensive repairs and additional journaled time for that vehicle.
To prevent these problems, always observe vehicle manual instructions regarding torque specifications. If a proper hand-calibrated torque wrench is used, combined with the required maintenance action, the vehicle will operate safely and efficiently.
How to read and interpret a wheel bearing torque chart?
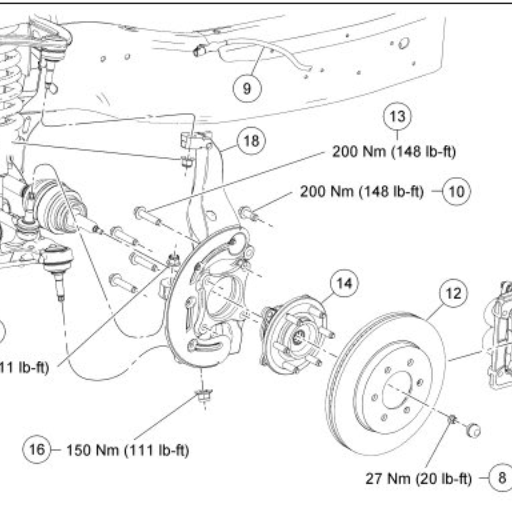
what I do first is to find out whether the wheel bearing torque chart is for a particular vehicle make and model. I have noticed in my experience that it will be easy to read a wheel-bearing torque once you get to know the vehicle model and its purpose. The next step is to find out the torque value in the foot-pound (ft-lbs) or Newton meter (Nm) that is used in the chart. Never forget to ask whether the lubricated or dry component is used. Such details, when applied, will ensure that the maximum amount of torque is applied without any risks to the safety and performance of the vehicle.
Decoding torque specifications for different vehicle makes and models.
When determining torque specifications, it is critical to note that there are differences from one vehicle maker to another; such differences may influence the accuracy and safety of the vehicle. To start with, the service manual, which is maintained by the manufacturer, has the most accurate torque values applicable to specific parts. Always confirm that the part is compatible by checking the numbers and whether such things as lubrication would change the value. Adhering to these suggestions enables you to use the correct torque that protects the vehicle and optimizes its operations.
Understanding the units of measurement (ft-lbs, Nm) in torque charts
It is my opinion that working with torque units such as foot pounds and Newton meters can bring precision into the mechanical world. To put it simply, Foot-pounds measure the torque force as imperial units spinning about a one-foot-long arm. On the other hand, Newton-meters are the same but in the metric system where a force is acted on the ne-meter arm. The relation between the two is quite simple: 1 ft-lb is equivalent to about 1.356 Nm. In a practical sense, knowing both measurements will make working with various tools and in various regions much easier as many places would have different torque specs from different sources and thus force one to learn how to apply correct measurements. Overall, understanding these units well will make the quality of any job much better.
What are the common torque specifications for wheel bearings?

Although in several vehicles, different torque specifications are set for the wheel bearings, in the case of standard cars and light trucks, one is advised to use 140 ft-lbs to 160 ft-lbs. However, it should be pointed out that not adhering to the required specification is also detrimental because over or under the recommended torque may lead to damage or failure of the system components at a later stage.
Typical torque ranges for passenger cars vs. trucks
When widening up my torque solutions for wheel bearings, it is never a bad idea to go back to the manufacturer’s instructions. Starting with small cars, for instance, the torque would normally be Application torque in the range of 100 to 150 ft-lbs. However, light trucks would probably require higher torques at around 150-200 ft-lbs or more. The specific ranges mentioned above are, however, subject to/factor in other actuals, but the main point is always to check the service manual because both under-tightening and over-tightening present their own range of problems ع, which is counter-productive, especially when you’re working with such a range of vehicles as light trucks and small cars.
Variations in torque specs for front wheel vs. rear wheel bearings
Due to differences in design and purpose, front and rear wheel bearings have different torque values. Front-wheel bearings are usually integrated into hub assemblies and designed for light loads, so they require fewer torques. On the other hand, rear wheel bearings are often under more stress, especially on rear wheel drive vehicles, and might require higher torques. Always consult the manufacturer’s service manual for torque values so that performance and safety are not compromised due to either under- or over-torqueing.
How do you properly torque wheel bearings during installation or replacement?

I appreciate that properly torquing the wheel bearings is vital and hence, I have a definite approach for it. To begin with, I would locate the appropriate service manual that has details on the designated torque for the vehicle’s bearings. If this is not done, it could result in setting up the torque incorrectly, which can lead to the bearings failing to hold up within a short time or even causing issues with how the vehicle is handled. For tightening the parts, I first start by setting the torque of the wrench to the value that is desired, during the tightening process this value is later refined and adjusted. Also, it is not advisable to utilize impact devices for this stage as they tend to be very harsh and can harm the bearing assembly. Finally, after the setup is done once, all the installation procedures are first cross-checked to confirm that the bearings are positioned well and that they rotate as intended. Employing these grades of care means a dependable and secure wheel-bearing introduction process every time.
Step-by-step guide to torquing wheel bearings
- Prepare the Tools and Workspace: Let’s begin with the work site – I like my workstation to be pristine and well organized. This means that all the tools I might need, such as a torque wrench, torque specifications sockets, proper vehicle parts, and instruction manuals, should be properly positioned strategically around me. Working in such fashion not only reduces time loss, but it also minimizes the chances of making mistakes.
- Check the Manufacturer’s Specifications: Once I have gathered every component for the work, the sample –representing the specific work I’ll be doing for the wheel bearing, I have to check for the torque instructions right after I check every manual I have because instructional material is crucial for accomplishing the task successfully.
- Gradual Tightening in Stages: I now have to tighten the bolts using the torque wrench. A cross pattern is often the most effective method to tighten nuts or bolts evenly. It can be especially useful in situations where uneven pressure can lead to damage or misalignment of components.
- Apply the Final Torque Setting: While moving toward the value I need to reach, I try to reach it with slight adjustments and shifting. If I realize that I have no other way to reach that targeting figure, I head towards using a crossing pattern for the bolts’ tightening method to eliminate chances of misalignment occurring as well as over-torquing the assembly, which would end up causing damage in the process.
- Verify Proper Installation: After the final steps of securing the wheel bearing have occurred, there is no doubt left in my mind that at the final overall assembly everything is intact. Just for safety measures, I loosen up and recheck the nuts with a wrench and do one last spin of the wheel to eliminate the chance of unexplainable friction or binding and hard, stiff movements to happen.
- Conduct a Final Inspection: In the end, I check the whole assembly by looking at it to see whether all of the nuts and bolts are in the correct places and have been properly tightened. Also, I clean the site where dirt or an excess of grease could impact functionality.
By following this structured process, I ensure the wheel bearings are torqued correctly, leading to safe and reliable operation on the road.
Essential tools for accurate wheel bearing torque application
Kicking off with the nut and bolt, one of the most vital and relatively easily designed and manufactured products of a wheel bearing assembly. The exact application of torque to the wheel bearing is essential. It’s also important to apply a serviceable push to the fasteners, and coming to the fastening devices, I would require quite a massive variety of sizes that are available in a good socket set. Lending torque angle is achieved by the application of a torque angle gage. For accurate measuring of how far a bolt may have been stretched, it may be a good idea to use a micrometer or an vernier caliper. Finally, a neat workspace and suitable tools for lubrication assist in the proper fitting of the parts, resulting in perfect performance. All these tools enable the best calibrations and fit on the wheel bearing while engaging in maintenance or installation activities.
Tips for adjusting wheel bearing preload
Preloading the wheel bearing is an important aspect in getting the longevity and performance out of the wheel assembly of a vehicle. Now, a general practice I consider is to find a middle ground: ‘ Not too tight, not too loose’. To begin, it’s essential to always adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines for preload values since these differ from one vehicle to another and from one application to another. Start by spinning the wheel hub while tightening the bearing nut; this will help align the bearings in their proper position. Next, undo a little bit and, using a torque wrench, re-tighten until it reaches the specified preload range, following the directive in the maker’s manual. While spinning the wheel, always note the turning feel of the bearing; if there are resistance or bumps, this may indicate some signs of problems. After completing the installation, it is important to check the preload from time to time; this is important to prevent overplay or overheating in the device when it is in operation. By following these measures, it can always guarantee safety and great performance practices for the long run.
What are the signs of improper wheel bearing torque?

Indicators of incorrect wheel bearing torque are too much clearance or slack, abnormal or uneven wear patterns on the tires, and abnormal sounds such as grinding or clicking noise originating from the wheel. Moreover, hub or bearing heat can be excessive, and fine-tuning the torque might be a headache. It becomes crucial to rectify these concerns in order to avoid any more damage to the vehicle and ensure the safety of the occupants.
Symptoms of over-tightened wheel bearings
I have seen something often occur, such as the use of over-tightened artificial shielding coupled with suspension mechanics. One notable instance of bearing weld deformation practically looks like a girdle around the mating surfaces, so to speak. This is coupled with over-tightened weld bolts, which, in turn, create some friction strain on the joints, such as rotating elements somewhere or pushing elements otherwise during mechanical movement. Not to mention the straining effects whirring or moaning joints produce. You’ll prevent this from ever happening again by adjusting the nuts and tightening them properly! This will help mitigate performance as well as safety.
Indicators of under-torqued wheel bearings
I have seen various cases in which wheel bearings were under-torqued, and they presented many challenges. To start with, if the torque is insufficient, then wheel bearings may not sit tight and would be loose, rendering them useless. Some key indicators to know that the wheel bearings might be under-torqued are:
- Excessive Play in the Wheel
Out of the many things that can go wrong within an automotive steering system, excessive wheel play is considered to be one of the most severe problems. This is typical of the bearing, which is never able to be clamped down onto any place.
- Clunking or Rattling Noises
Under-torqued bearings rot in the corner, causing clanging or rattling sounds; as a result, driving on a corner or on uneven roads can add extra pressure on the components, causing noise. This noise conveys an important message that something is loose and should be addressed.
- Premature Wear and Tear
Bearing wear tends to result from improper influence concentration, which leads to force mismatching across the bearing elements. This shifting, without proper adjustment, can cause early breakdown not only in bearing parts but also in its attachments, including hubs or axels.
- Irregular Tire Wear
Bore bearings placed at the wrong tightening angle can set the wheel to the abrupt angle position. This mechanism, over time, induces irregular rubbing of the tires on the road, which not only damages the tire but affects the performance and safety as well.
- Vibration When Driving
Barely fixed bearings make the mechanism either partly loose or too tight, and without much support, this wobbling connects the wheel and hub assembly in the end, causing quakes that easily cause the steering wheel to rattle as well and bite through the flooring.
The manufacturer’s torque specifications should be observed as indicated by each of these pointers. It is with emphasis that a torque tool is always utilized to the calibrated settings, and the specified torque parameters for the particular vehicle should be observed at all times.
Where can I find wheel bearing torque specifications for my specific vehicle?
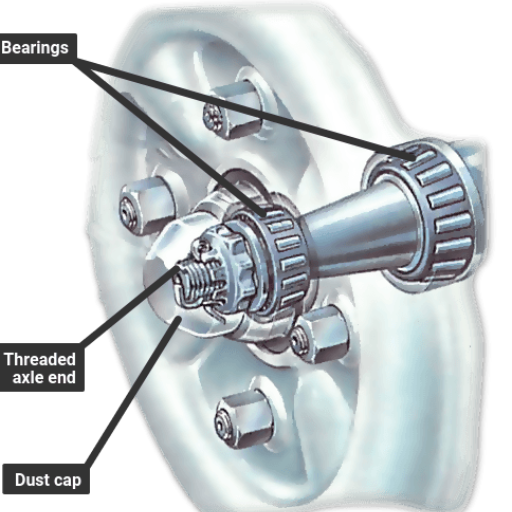
You can see the wheel bearing torque specs of your specific car in a number of credible publications. An automotive service manual is the primary point of reference for quite a number of vehicle proprietors because it serves as the most appropriate and also approved source. If you don’t have the manual, many manufacturers’ models show the same strategy on their websites or through Customer service. What’s more, reliable web based motor vehicle repair services or databases such as those in use by auto mechanics are better options. Always make sure the source is specific to your vehicle in terms of make, model, and year for optimum accuracy. Since torque is crucial, there is no harm in spending a little more time verifying the regions you used to reference.
Reliable sources for torque charts and specifications
To avoid all unnecessary risks and especially on the safe side, it is best to always refer to the manufacturer’s official service manuals when looking for reliable torque specifications or charts specific to your vehicle, as This means that the values listed in the manual are legally approved and are pertinent to all vehicle owner’s manuals. In the absence of such a manual, however, the basic manufacturer’s site or the customer support center should suffice. Other options, which, of course, are trusted, are professional repair platform sites like ALLDATA or Mitchell1, which target industry mechanics and provide accurate and relevant information about the necessary makes and models.
Using online forums and manufacturer websites for torque information
I know from my experience that manufacturer websites would come in handy when searching for torque specification numbers. Such documents are usually official and get straight to the point. However, with regard to the forums, I suggest rather a careful approach. Sure, there is practical knowledge on topics from people who are passionate about their cars or are professional mechanics, but these forums give unverified and inaccurate information more often than not. To ensure accuracy and to avoid any potentially fatal errors, it is important to verify any torque values with an authoritative reference, such as the service manual or a reputable repair website.
How often should wheel bearing torque be checked and adjusted?

Important vehicle components like wheel bearings require special handling. Whether routine maintenance or servicing is carried out, the torque should be measured and changed accordingly. On vehicle maintenance routines, brake inspections and tire rotation occur from 6000 – 12000, depending on the particulars of the car, the former to the latter. It’s advisable to always check the service manual of your car to get the instructions and intervals recommended by the manufacturer for wheel bearing torque to enhance the efficiency of the vehicle.
Recommended maintenance intervals for wheel bearing torque inspection
In the industry, when a client brings his vehicle in for service, I advise checking the wheel bearing torque at intervals of 16000 Kms and if there are obvious signs of excessive noise, movement or abnormal pulling from the tires, then at a much earlier date. When a client rotates the tires or has the brake serviced, it’s a great time to adjust and check bearing torque because those kinds of services usually coincide. The right level of torque not only increases the lifespan of the bearing but also contributes significantly to the vehicle’s safety and performance. In any case, the servicing manual of the vehicle should be referred to for detailed steps applicable to the vehicle in question.
Factors that may necessitate more frequent torque checks
It’s likely that you’ll need it if you drive in extreme situations such as heavily off-roading, getting your vehicle wet or exposed to corrosive substances, or more extreme loads and towing. Frequent acceleration and deceleration of your vehicle would also justify more inspections, as would uneven wear on your tires or, even more so, any strange sounds coming from the wheels or tire region. Of all these scenarios, it is smart to take care of bearing inspection more frequently as that precaution will avoid any larger problems that could arise and ensure much better performance and safety.
Reference
- Torque specification guide by SKF – This guide provides detailed torque specifications for wheel bearings.
- STEMCO Endorses TMC’s Recommended Wheel Bearing Adjustment – Offers insights into the recommended procedures for wheel bearing adjustments.
- SKF Torque specification guide on caissiedrive.net – Another comprehensive guide on torque specifications for wheel bearings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the importance of proper wheel bearing nut torque?
A: Proper wheel bearing nut torque is crucial for ensuring the longevity and safety of your vehicle’s wheel bearings. Correct torque prevents excessive play, reduces wear, and maintains proper bearing adjustment. Improper torque can lead to premature bearing failure, wheel wobble, or even catastrophic wheel detachment.
Q: How do I find the correct torque specifications for my vehicle’s wheel bearing nut?
A: To find the correct torque specs, consult your vehicle’s service manual, a Haynes manual, or a reputable online database. Torque specifications can vary significantly between makes and models, so it’s essential to use the correct information for your specific vehicle, whether it’s a Ford, Chevy, Subaru, or any other brand.
Q: What tools do I need to properly torque a wheel bearing nut?
A: Essential tools include a torque wrench, the correct size socket for your axle nut, and possibly a breaker bar for initial loosening. For some vehicles, you may also need a special tool to lock the hub or spindle while tightening. Always use the appropriate tools to avoid damaging components or achieving incorrect torque.
Q: How do I adjust wheel bearings on a vehicle with adjustable bearings?
A: For adjustable bearings, start by tightening the inner nut to the specified torque. Then, back off the nut as indicated in your vehicle’s manual (often 1/4 to 1/2 turn). Install the lock washer and outer nut, tightening to the specified torque. Finally, check for proper bearing play by spinning the hub and ensuring there’s no excessive movement.
Q: What’s the typical torque range for wheel bearing nuts?
A: Torque specifications can vary widely, typically ranging from 50 to 300 ft-lbs (68 to 407 Nm). For example, some vehicles might require 103 ft-lbs, while others may need much higher torque. Always refer to your specific vehicle’s torque specs, as using an incorrect value can lead to bearing failure.
Q: How do I know if I’ve achieved the correct wheel bearing adjustment?
A: After torquing the nut to spec, spin the wheel hub. It should rotate smoothly without any grinding or catching. There should be no noticeable play when you try to move the wheel vertically or horizontally. If you’re unsure, it’s best to have a professional mechanic check your work.
Q: Are torque procedures different for 4×4 or 4WD vehicles?
A: Yes, 4×4 and 4WD vehicles often have different procedures due to their more complex drivetrain. These vehicles may have auto hubs or manual locking hubs, which can affect the torque procedure. Always consult the specific instructions for your 4×4 or 4WD vehicle, as improper torque can damage not only the bearings but also other drivetrain components.
Q: How often should wheel bearing nuts be checked and re-torqued?
A: It’s good practice to check wheel bearing nut torque annually or every 12,000 miles, whichever comes first. Additionally, always re-check the torque after any work involving wheel removal or bearing service. If you notice any unusual noise, vibration, or steering issues, check the bearing adjustment and torque immediately.
Q: Can I use a standard socket instead of a specialized axle nut socket?
A: While it’s possible to use a standard socket in some cases, a specialized axle nut socket is recommended. These sockets are designed to withstand the high torque values required for axle nuts and provide better fit and grip. Using the correct tool reduces the risk of damaging the nut or rounding off its edges.
Q: What should I do if I’m unsure about torquing my wheel bearing nuts?
A: If you’re unsure about the process or don’t have the proper tools, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic or your vehicle’s dealer. Proper wheel bearing adjustment is critical for safety, and incorrect torque can lead to expensive repairs or dangerous driving conditions. When in doubt, seek expert assistance to ensure the job is done correctly.
